Japan has decided to apply foreign trade regulations to chipmaking equipment as part of its efforts to secure stable supply chains, the Finance Ministry said Friday.
Foreign investors are now required to give prior notice when conducting direct investment in equipment tied to chipmaking, including when acquiring a 1% or bigger stake in a listed company or buying shares in an unlisted company, the ministry said in a statement, according to Bloomberg.
The move also aims to address the risk of technology leakage and keep commercial technologies from being used for military purposes, it said.
Other products added to the list of so-called “core business sectors” include advanced electronic components, machine tool components, marine engines, fiber optic cables and multifunctional machines, according to the ministry.
The targeted move will help the government enhance national security while its impact on companies is expected to be limited, a Finance Ministry official told Bloomberg.
The move comes as Japan tries to revive its own capacity to produce semiconductors as a pillar of its economic security strategy.
Japan has already earmarked some ¥4 trillion ($26.9 billion) over the last three years to recharge its semiconductor sectors and promote digitalization.
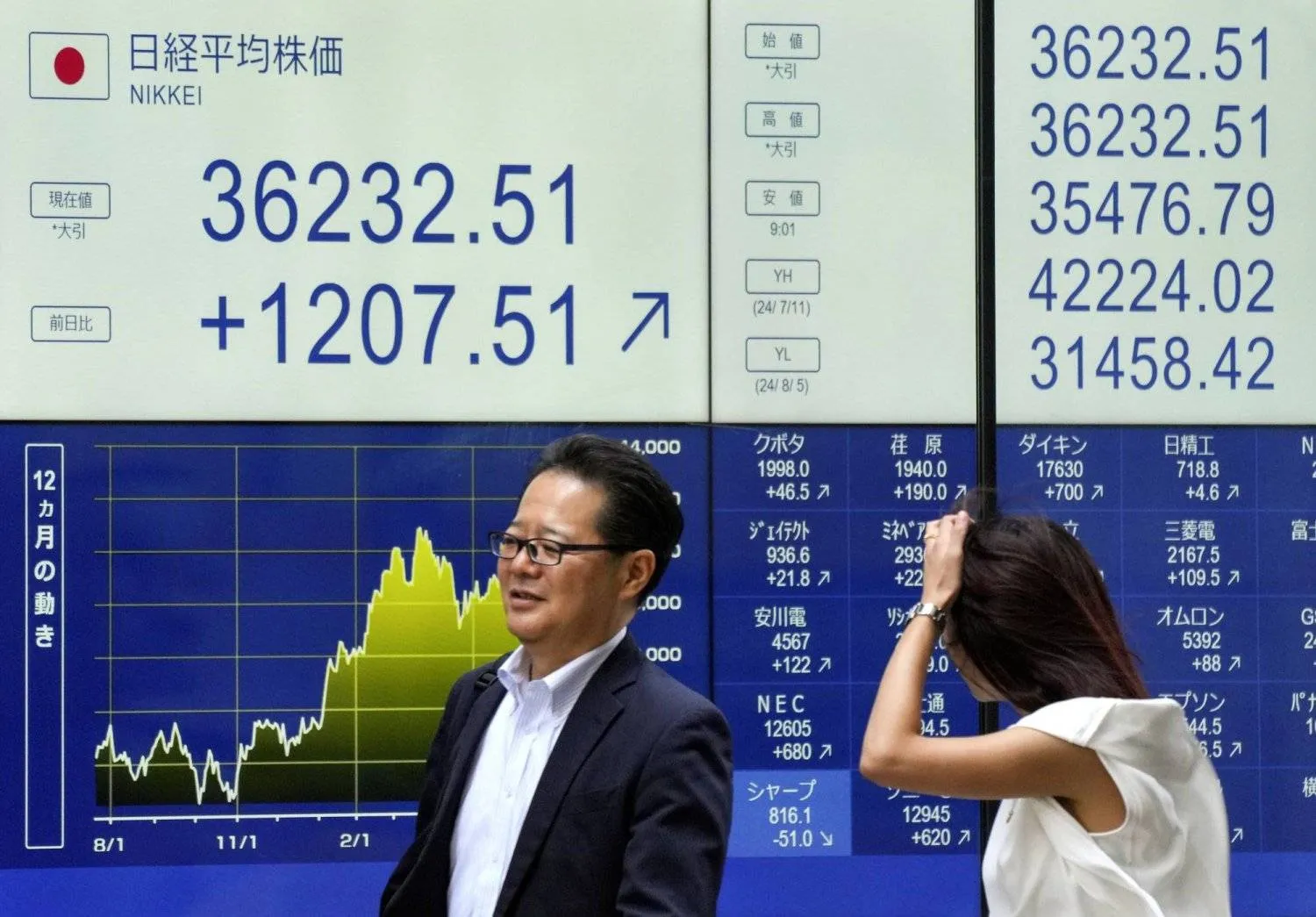
In the markets, Japan's Nikkei share average climbed nearly 3% on Friday and notched its best week in more than four years, as strong US retail sales data soothed fears of a recession in the world's largest economy and Japan's top trading partner.
The Nikkei closed 3.6% higher at 38,062.67, locking in its second-largest daily gain for the year, while the broader Topix finished up about 3% at 2,678.60.
The Nikkei logged its biggest weekly gain since April 2020, rising over 8%, buoyed by easing concerns about the state of the US economy, a pause in the yen's rapid appreciation and a pick-up in Japan's economic growth.
Wall Street's main indexes closed higher on Thursday after US retail sales increased 1% in July following a downwardly revised 0.2% drop in June.
The rally was broad-based, with 219 of the Nikkei's 225 constituents advancing against 5 decliners, while shares of many big names surged.
Nikkei heavyweight Fast Retailing jumped 6.2%, while chip-related share Tokyo Electron gained 4.8%, along with peer Advantest, adding 6.8%.
Meanwhile, the yen weakened against the dollar overnight in a boost to Japan's export-related shares like automaker Toyota Motor, which rose about 2%.
The Nikkei fell more than 12% on Aug. 5 in its biggest single-day decline since Black Monday amid a storm of concerns, including US recession fears sparked by a weak jobs report and a sharply stronger yen.
It has since clawed back those losses but remains well off an all-time peak of 42,426.77 touched in mid-July.
Among individual shares on Friday, electrical component maker Fujikura rallied over 11% to become the biggest percentage gainer.