Amna Ishaq can no longer feed her children "more than once a day and sometimes not at all" after nearly a year of devastating war in Sudan.
"We are all sick, along with our children. We have nothing to eat and the water we find is polluted," Ishaq told AFP at a camp for the displaced in Darfur.
The vast western region is no stranger to war, suffering devastation in a deadly conflict that began in 2003 and which also sparked a hunger crisis.
With war returning to Sudan last April, the United Nations has warned that "an entire generation could be destroyed".
The world body says millions of displaced children are starving, have been forced into marriage or become child soldiers and threatened with death.
The fighting broke out on April 15, 2023 between Abdel Fattah al-Burhan's army and Mohammed Hamdan Daglo's Rapid Support Forces (RSF).
Looting, fighting, air strikes and roads cut by warring factions have isolated every region of Sudan, a northeast African country more than three times the size of France.
The UN says it has been able to reach only 10 percent of Sudan's 48 million people, with the country on the brink of famine.
At Otach, a displacement camp set up two decades ago in South Darfur where Ishaq has taken refuge with her family, rations of maize porridge no longer arrive.
About "222,000 children could die of starvation within a few weeks or months" and "more than 700,000 this year", according to the UN.
Doctors Without Borders (MSF) said that at least one child dies every two hours at North Darfur's Zamzam displacement camp alone.
And at Kalma camp in South Darfur, the aid group Alight said that "more than two children are dying every 12 hours".
Children have been sold
Medical journal The Lancet has reported that the small Al-Buluk pediatric hospital in the capital Khartoum admits "about 25 children for severe acute malnutrition. Each week, two or three of them die."
Overall, nearly three million children are suffering from malnutrition and 19 million are no longer in school, according to Save the Children, endangering the future of a nation where 42 percent of the population is under 14 years old.
Even before this war, nearly half of Sudan's children had severely reduced growth and 70 percent were unable to read and understand a simple sentence, the charity says.
Adam Regal, spokesman for independent Sudanese aid group General Coordination for Refugees and Displaced Persons in Darfur, said he has seen dozens of children die.
He blamed "the stubbornness" of the warring parties, telling AFP that "food and humanitarian aid no longer arrive" because of a lack of access.
A Khartoum factory that produced nutritional supplements for children has been destroyed by bombing and vaccine factories for newborns have been looted.
Cholera, measles and malaria prevail in eastern parts of the country.
Adding to the health crisis are the horrors of war.
More and more Sudanese organizations are warning that to feed their children parents are resorting to "selling" some of them.
One local charity reported that a father sold his 15-year-old daughter for a few bags of grain at a market.
The UN has also recorded child marriages in response to "family separations" -- mothers or fathers who have lost their spouses or children while fleeing violence in panic -- or because of "gender-based and sexual violence including rape and unwanted pregnancies".
Rape and child soldiers
The UN said young girls and women have been the victims of "abductions, forced marriages, and sexual violence related to the conflict in Darfur and in the state of Al-Jazira" south of Khartoum, where many displaced people are.
The dangers facing boys are different: both the army and the paramilitaries, but also tribal and ethnic militias, "recruit and use children in Darfur, Kordofan, Khartoum, and in the east of the country", the experts said.
Some parties even force "children from a neighboring country to actively participate in hostilities", they added.
Since the early days of the war, videos uploaded by soldiers and paramilitaries regularly show teenagers on military pickup trucks or with automatic rifles in hand.
It's the "catastrophe of a generation", UN officials said.
Generation War: Children in Sudan Today
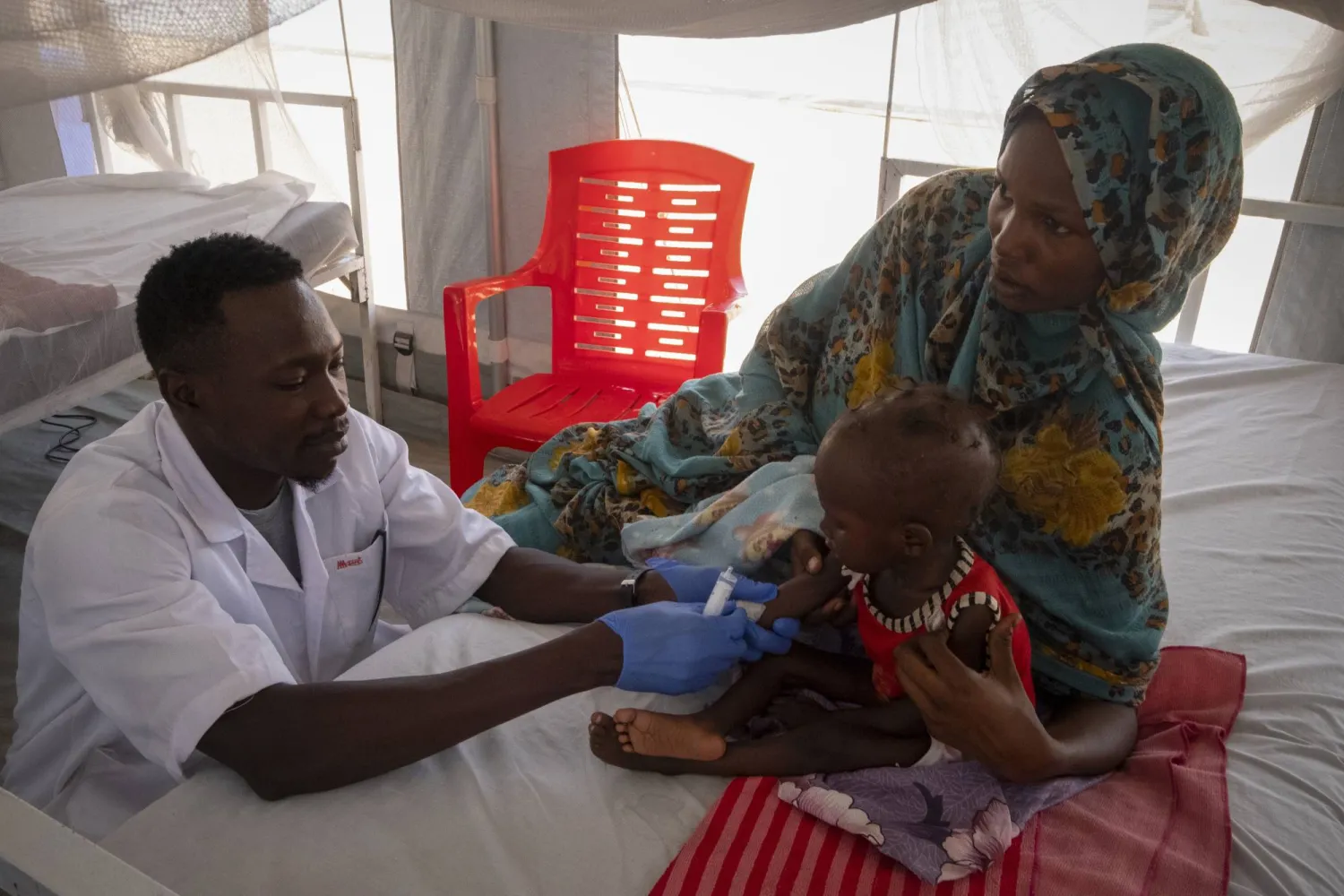
A refugee mother from Darfur in Sudan holds her son during his medical exam, at the hospital set up by the NGO Doctors Without Borders (MSF) in the refugee camp of Metche, eastern Chad, 05 April 2024. EPA/STRINGER

Generation War: Children in Sudan Today

A refugee mother from Darfur in Sudan holds her son during his medical exam, at the hospital set up by the NGO Doctors Without Borders (MSF) in the refugee camp of Metche, eastern Chad, 05 April 2024. EPA/STRINGER
لم تشترك بعد
انشئ حساباً خاصاً بك لتحصل على أخبار مخصصة لك ولتتمتع بخاصية حفظ المقالات وتتلقى نشراتنا البريدية المتنوعة












