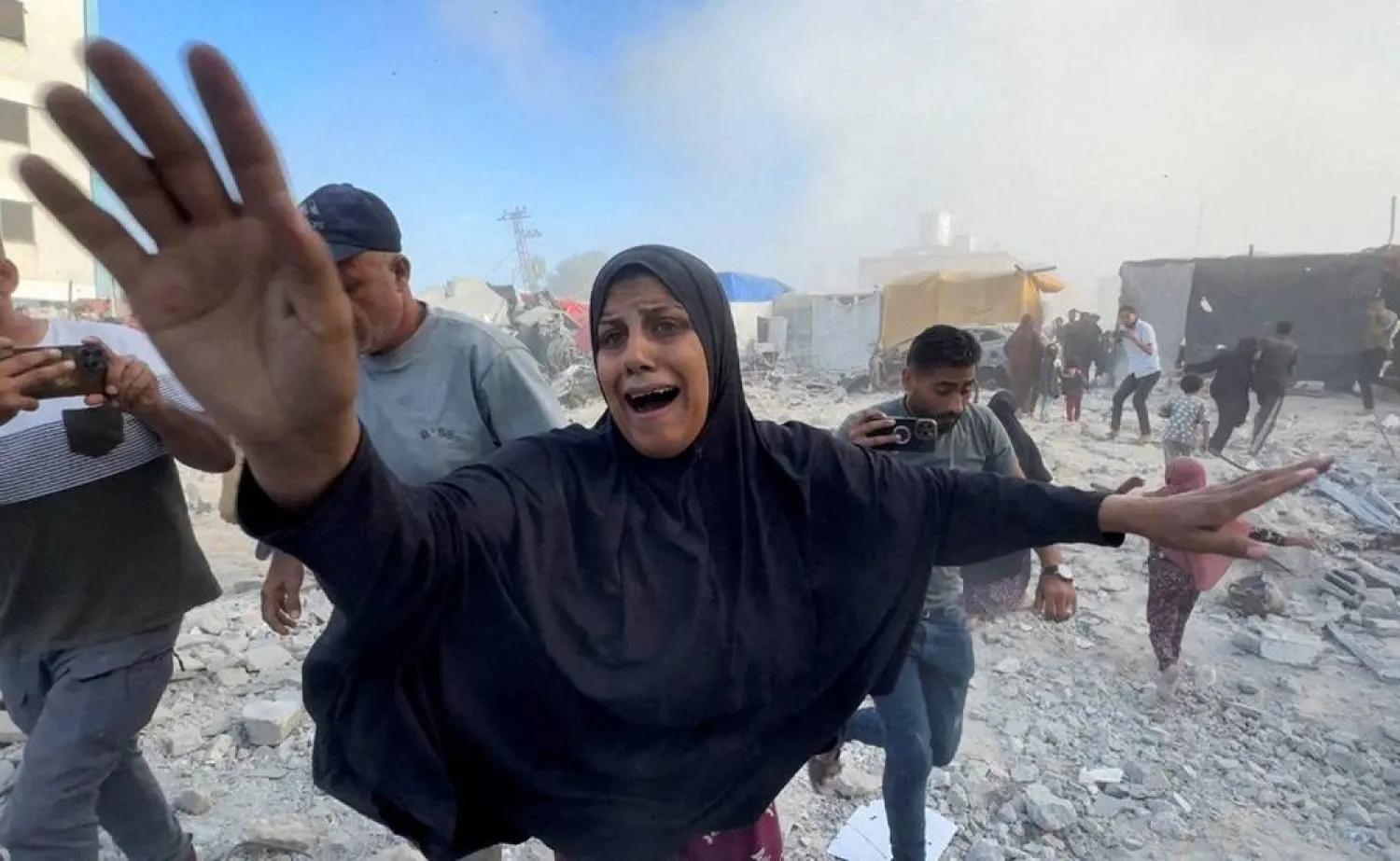
An Israeli airstrike slammed into a residential building next to the main medical center in Gaza’s southern city of Khan Younis, wounding at least seven people, hospital authorities and witnesses said Wednesday.
Nasser Hospital sits in the western part of the city, which is inside the Israeli-designated humanitarian “safe zone” where Palestinians have been told to go, according to maps provided by Israel's military. The latest Israeli evacuation order affected about 250,000 people earlier this week across wide swathes of Gaza, the United Nations estimated.
As dust from Wednesday's strike billowed through a street near Nasser Hospital, an Associated Press contributor filmed people running in all directions — some rushing toward the destruction and some away. Men carried two young boys, apparently wounded. Later, civil defense first responders and bystanders picked their way across chunks of cement and twisted metal, searching for people who might have been buried.
Displaced families ordered out of eastern Khan Younis on Monday have struggled to find places to live in overcrowded shelters and open areas in the western parts of the city. Wednesday's airstrike hit an area that also includes a school-turned-shelter for displaced people, many of whom are living in makeshift tents.
“We were sitting in this tent, three people, and we were surprised by the rubble and dust,” said one man, Jalal Lafi, who was displaced from the city of Rafah in the south.
“The house was bombed without any warning, hit by two missiles in a row, one after another,” he said, looking back over his shoulder at the rubble, his hair and clothes covered in grey soot.
The Israeli military did not immediately comment on the strike.
Andrea De Domenico, the head of the UN humanitarian office for the Palestinian territories, said Gaza is “the only place in the world where people cannot find a safe refuge, and can’t leave the front line.” Even in so-called safe areas there are bombings, he told reporters Wednesday in Jerusalem.
An Israeli airstrike Tuesday killed a prominent Palestinian doctor and eight members of his extended family, just hours after they complied with military orders to evacuate their home and moved to the Israeli-designated safe zone.
Most Palestinians seeking safety are either heading to a coastal area called Muwasi or the nearby city of Deir al-Balah, De Domenico said.
The Israeli military said Tuesday it estimates at least 1.8 million Palestinians are now in the humanitarian zone it declared, covering a stretch of about 14 kilometers (8.6 miles) along the Mediterranean. Much of that area is now blanketed with tent camps that lack sanitation and medical facilities with limited access to aid, UN and humanitarian groups say. Families live amid mountains of trash and streams of water contaminated by sewage.
It’s been “a major challenge” to even bring food to those areas, De Domenico said. Although the UN is now able to meet basic needs in northern Gaza, he said it’s very difficult getting aid into the south. Israel says it allows aid to enter via the Kerem Shalom crossing with southern Gaza, and blames the UN for not doing enough to move the aid.
The UN says fighting, Israeli military restrictions and general chaos — including criminal gangs taking aid off trucks in Gaza — make it nearly impossible for aid workers to pick up truckloads of goods that Israel has let in.
The amount of food and other supplies getting into Gaza has plunged since Israel’s offensive into Rafah began two months ago, causing widespread hunger and sparking fears of famine.
“It’s an unendurable life,” said Anwar Salman, a displaced Palestinian. “If they want to kill us, let them do it. Let them drop a nuclear bomb and finish us. We are fed up. We are tired. We are dying every day.”