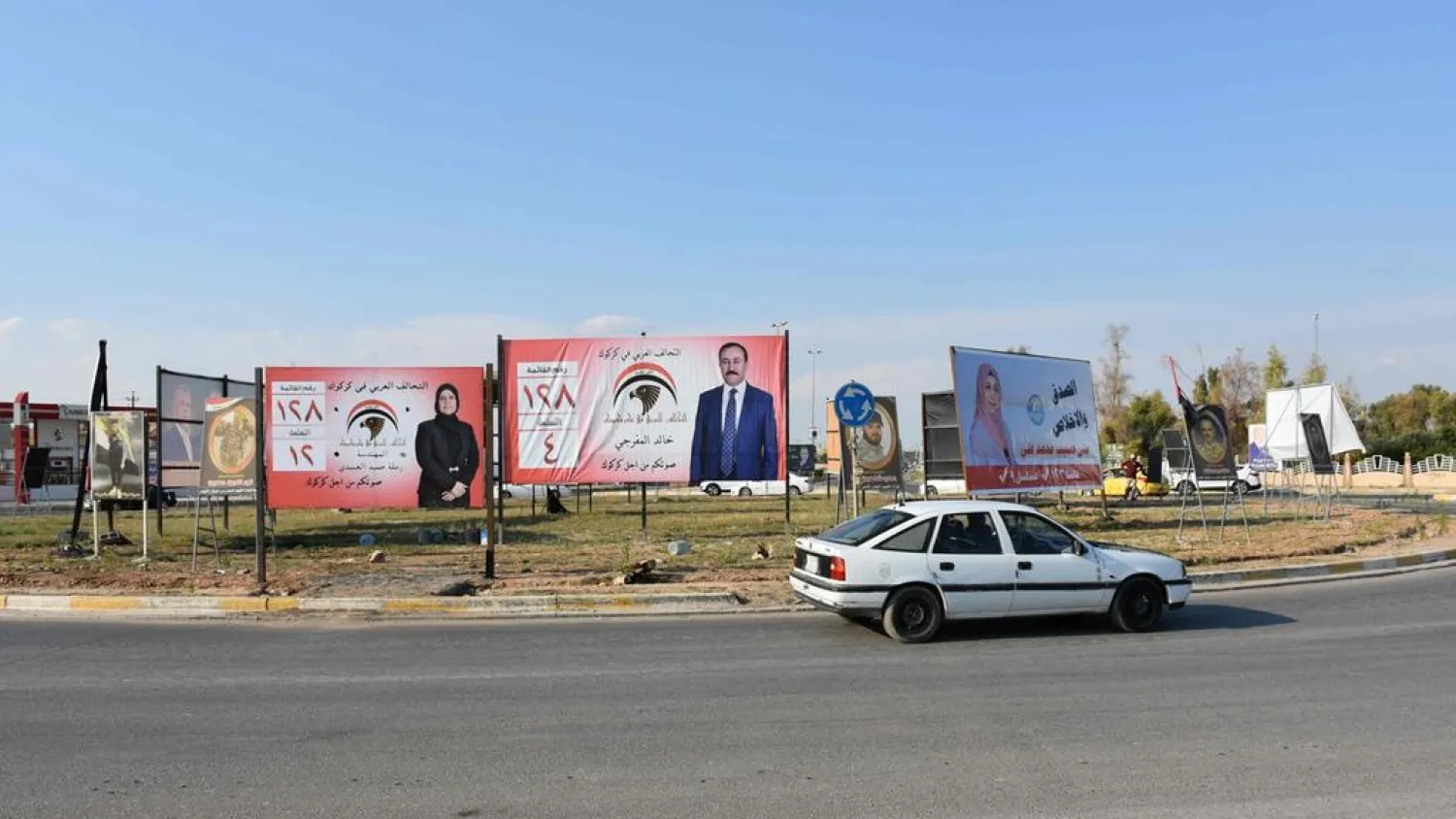
The electoral campaigns in the northern city of Kirkuk differ completely from the scenes in other Kurdistan Region provinces and perhaps even the rest of Iraq.
Asharq Al-Awsat toured the city, which has been covered wall-to-wall with electoral posters. They have taken on a nationalist and sectarian edge, which reflects the deep partisan divides and conflicts among the various ethnicities that make up the region.
Dozens of political forces are running in the May 12 elections and various Kurdish, Arab, Turkmen, Chaladean and Assyrian alliances have been formed with the goal of winning the largest number of seats at parliament. They are competing for 12 seats that are dedicated to the Kirkuk province.
The security presence is also palpable on the streets with the heavy deployment of security forces, local and federal police, anti-terrorism units and even the Popular Mobilization Forces militias.
The division among the political powers and their popular bases is clear to see on the ground where neighborhoods reflect the identity of their main residents. In Arab neighborhoods, one only sees posters of Arab candidates and movements.
In Kurdish areas, Kurdish candidates have been barred from raising the flag of Kurdistan. The flag has even been banned from electoral posters and the region is not referred to in any campaign speeches. Candidates are not allowed, even implicitly, to refer to the “Kurdish identity of Kirkuk.”
The largest Kurdish movement, the Kurdish Democratic Party, headed by former President Masoud Barzani, has meanwhile decided to boycott the elections in disputed areas. They include the Diyala, Kirkuk and Salaheddine provinces, which the party says are occupied by Iraqi forces. The party has consequently decided to only field candidates in the Nineveh province.
Arab alliance candidate Hatem al-Tai said that the law ensures the right for everyone to carry out an electoral campaign in Kirkuk without discrimination. He noted however that the main groups, the Kurds, Arabs and Turkmen, have traded accusations that their posters have been torn down.
He told Asharq Al-Awsat: “Some meddlers, who do not represent a particular side, have torn down candidate posters. I, myself, have been a victim of these actions.”
He also accused partisan powers, often either Turkmen or Kurdish, of deliberately taking down posters.
He added, however, that candidates are free to promote themselves in all neighborhoods and the law guarantees this right.
The Arab platform, Tai said, is based on committing to Iraq’s unity and the Iraqi identity of Kirkuk.
Head of the Turkmeneli Party, Riyad Sari Kahya said it was not necessary for a Kurdish candidate to promote himself in Turkmen or Arab neighborhoods in order to avoid stoking tensions. Similarly, candidates from these ethnicities should not promote themselves in rival areas.
Kirkuk can do without such tensions during this time so that the electoral process can run smoothly and safely, he stressed. The competition between the various ethnicities and parties should take into consideration the sensitive situation, especially in Kirkuk.
On his party’s electoral platform, he said: “We will primarily seek permanent peace between the powers that comprise the main forces in Kirkuk.”
“We will then adopt a new agenda that calls for establishing the autonomy of the Kirkuk region,” he added. This can be achieved through the support of the federal authorities in Baghdad and Kurdistan Region through a joint understanding between all sides.
Patriotic Union of Kurdistan candidate Almas Fadel al-Agha remarked that Kurdish candidates are facing “major obstacles” in Kirkuk. She cited the exclusion of Kurdish forces from ensuring the security of the city and the tearing down of Kurdish candidate posters in non-Kurdish regions.
She demanded the redeployment of the Kurdish Peshmerga and security forces and the return of thousands of Kurdish refugees back to their region “otherwise the elections here will be unbalanced.”
She explained that thousands of refugees have not returned to their homes in Kirkuk, Tuz Khurmatu, Daquq and other regions.
“There inability to take part in the voting will negatively impact the chances of the Kurdish powers in the elections and we predict that they will lose seats in parliament as a result. The Kurdish voters however are excited to head to polls to prove their presence in the area,” she stressed.