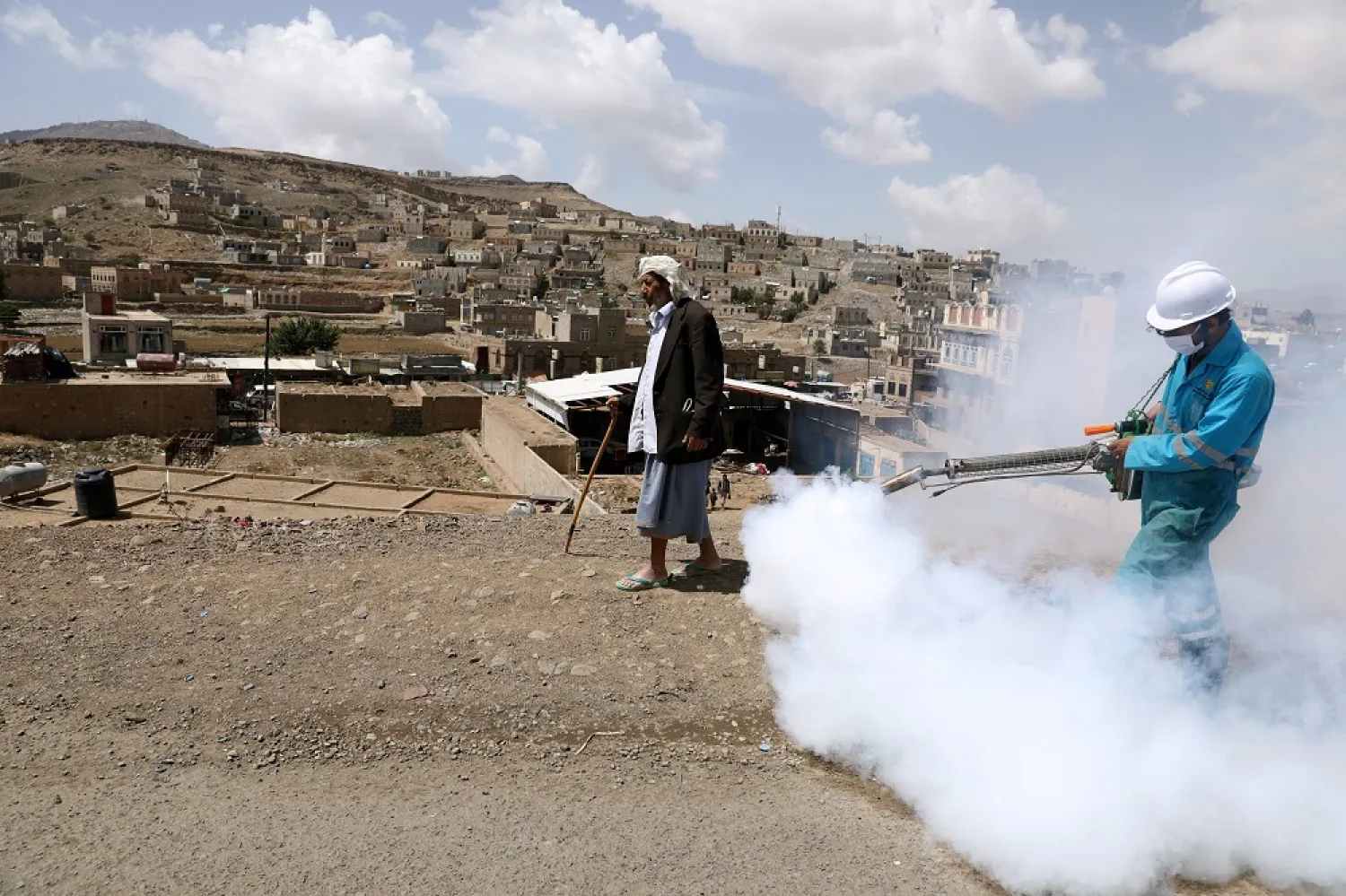
Yemeni activists and healthcare professionals in regions held by the Houthis accused the Iran-backed militias of killing coronavirus patients in quarantine and later burying them in secret.
Activists on social media posted photos of mass graves in Sanaa where the patients are being buried. The Houthis, meanwhile, continue to refuse to acknowledge the pandemic, despite assertions by medical sources that dozens of people have died from the virus and that quarantine wards in hospitals are full.
The sources revealed that confirmed cases are referred to quarantine at Sanaa’s Kuwait and Zayed Hospitals and the Jabla Hospital in the Ibb province, only to leave in body bags the next day.
Secret burials
A medical source told Asharq Al-Awsat that one patient was transferred to quarantine in Zayed Hospital only to die hours after being admitted, raising suspicions that the Houthis were killing the patients.
Residents and some healthcare professionals in Sanaa have said that the Houthis have allegedly ordered medical staff to euthanize coronavirus patients. Asharq Al-Awsat has not been able to verify the claims.
Activists in Ibb, 170 kilometers south of Sanaa, said that a father and his son died within a day of each other after being admitted to quarantine in Jabla Hospital.
Witnesses in Ibb city said that days ago, the Houthis had secretly buried several people during a dawn burial. They suspected that the deceased had died from the coronavirus.
The militias are very keen on denying that the virus had spread in areas under their control. Their appointed health minister, Taha al-Moutawakel, said on Saturday that two patients had recovered from the disease, while two have died.
He tried to ease growing concern among the people, saying the Houthis will only reveal information about recoveries.
Such secrecy has sparked outrage even among the militias’ support base, especially after doctors loyal to the Houthis have died from the coronavirus.
More images posted on social media showed Houthis wearing protective gear standing by recently dug graves with an ambulance nearby as they prepared for burial.
Intimidation and terror
In a sign of even more Houthi recklessness with the lives of the people, medical sources accused the militias of threatening medical staff, hospitals and citizens against spreading information about the outbreak.
The Houthis have gone so far as to confiscate the telephones of doctors to prevent them from sharing news about the virus cases.
Activists and doctors described “catastrophic” conditions in Houthi-held regions, with people suspected of suffering from coronavirus collapsing on the streets.
Furthermore, the Houthis have yet to take any serious preventive measures, such as shut busy markets and impose social distancing. They fear that such restrictions will impact the economy and money flowing into their pockets.
This negligence has only created a sense of terror in Sanaa. The people are now not only worried about contracting the virus, but how the Houthis would react to a suspected case. Activists said that the militias do not send medical teams to suspected cases, but security forces instead.
Meanwhile, 65 doctors in Houthi-held regions addressed a statement to Moutawakel, confirming that the virus cases and fatalities were “rising day after day”. They criticized the disregard of preventive measures by people in self-isolation and quarantine, as well as in markets and mosques.
They urged authorities to be transparent about the outbreak and help protect medical staff that are treating patients and avoid terrorizing people, who are forced to hide suspected virus cases.