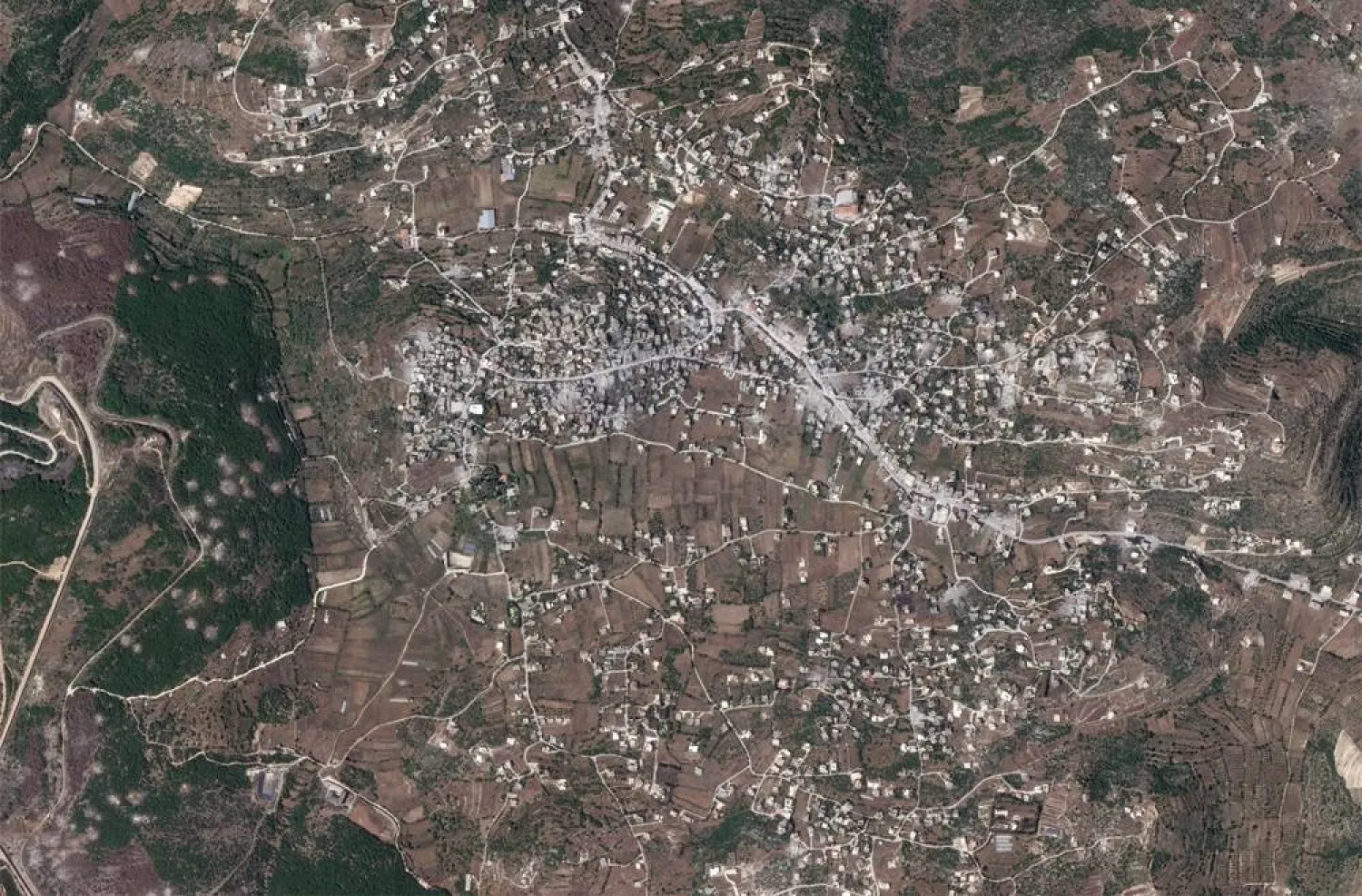
Satellite images showing much of the Lebanese village of Aita al-Shaab in ruins after months of Israeli air strikes offer a glimpse of the scale of damage in one of Hezbollah's main bastions in south Lebanon.
The images from private satellite operator Planet Labs PBC, taken on June 5 and analyzed by Reuters, show at least 64 destroyed sites in Aita al-Shaab. Several of the sites contain more than one building.
Located in southern Lebanon where Hezbollah enjoys strong backing from many Shiites, Aita al-Shaab was a frontline in 2006 when its fighters successfully repelled Israeli attacks during the full-scale, 34-day war.
While the current fighting between Israel and the Iran-backed Shiite movement is still relatively contained, it marks their worst confrontation in 18 years, with widespread damage to buildings and farmland in south Lebanon and northern Israel.
The sides have been trading fire since the Gaza war erupted in October. The hostilities have largely depopulated the border zone on both sides, with tens of thousands of people fleeing their homes.
The destruction in Aita al-Shaab is comparable to the damage done in 2006, a dozen people familiar with the damage said, at a time when escalation has prompted growing concern of another all out war between the heavily-armed adversaries.
Reuters does not have satellite images from 2006 to compare the two periods.
Israel says fire from Lebanon has killed 18 soldiers and 10 civilians. Israeli attacks have killed more than 300 Hezbollah fighters and 87 civilians, according to Reuters tallies.
At least 10 of Hezbollah's dead came from Aita al-Shaab, and dozens more from the surrounding area, according to Hezbollah death notices reviewed by Reuters. Six civilians have been killed in the village, a security source said.
The village, just 1 km (0.6 miles) from the border, is among the most heavily bombarded by Israel, Hashem Haidar, the head of the government's regional development agency the Council for South Lebanon told Reuters.
"There is a lot of destruction in the village center, not just the buildings they hit and destroyed, but those around them" which are beyond repair, said Aita al-Shaab mayor Mohamed Srour.
Most of the village's 13,500 residents fled in October, when Israel began striking buildings and woodland nearby, he added.
The bombing campaign has made a swath of the border area in Lebanon "unfit for living," Haidar said.
The Israeli military has said it has hit Hezbollah targets in the Aita al-Shaab area during the conflict.
In response to Reuters questions, Israeli military spokesperson Nir Dinar said Israel was acting in self-defense.
Hezbollah had made the area "unlivable" by hiding in civilian buildings and launching unprovoked attacks that made "ghost towns" of Israeli villages, Dinar said.
"Israel is striking military targets, the fact that they're hiding inside civilian infrastructures is Hezbollah's decision," Dinar said.
The military did not give further details of the nature of its targets in the village. It said Hezbollah was escalating attacks, firing over 4,800 rockets into northern Israel, "killing civilians and displacing tens of thousands."
Hezbollah's media office did not immediately respond to requests for comment.
Hezbollah has said that displacing so many Israelis has been an accomplishment of its campaign.
'CONTINUING THREAT'
The current conflict began a day after the Oct. 7 Hamas attacks on Israel, when Hezbollah opened fire in solidarity with its Palestinian ally. Hezbollah has said it will stop when the Israeli assault on Gaza ends.
Aita al-Shaab is perched on a hilltop looking into Israel and is one of many Shiite villages experts say are Hezbollah's first line of defense against Israel.
The 2006 war started when Hezbollah fighters infiltrated Israel from an area near Aita al-Shaab, capturing two Israeli soldiers.
A source familiar with Hezbollah's operations said the village had played a strategic role in 2006 and would do so again in any new war. The source did not give more details of the group's activities there.
Hezbollah fighters held out in the village for the entire 2006 war. An Israeli-government appointed inquiry found that Israeli forces failed to capture it as ordered, despite encircling the village and dealing a serious blow to Hezbollah. Anti-tank missiles were still being fired from the village five days before the war ended, it said.
Seth G. Jones, senior vice president at the Center for Strategic and International Studies in Washington, said the area was militarily important in several ways, allowing Hezbollah to fire its shorter-range rockets into Israel.
"If there was a ground incursion, these would be frontline locations for Hezbollah to defend, or to try to attrite" Israeli forces, he said.
Hezbollah, far stronger than in 2006, has announced attacks on targets directly across the border from Aita al-Shaab during the current hostilities, including in the Israeli village of Shtula 1.9 km (1.18 miles) away and nearby areas.
Satellite images of Shtula and nearby Israeli villages taken on June 5 do not show visible damage to buildings. Israel's Defense Ministry said 60 homes in Shutla had been damaged including 11 severely damaged, according to a May report by newspaper Calcalist. The ministry did not respond to Reuters requests for data.
Throughout northern Israel, around 2,000 buildings have been damaged, the country's tax authority said. Across the border, some 2,700 homes have been completely destroyed and 22,000 more damaged, significantly below the 2006 conflict, the Council for South Lebanon said, though these numbers were preliminary.
Fires sparked by the fighting have affected hundreds of hectares of farmland and forest either side of the border, authorities said.
HEAVY ORDNANCE
Andreas Krieg of King's College in London said the structural damage in Aita al-Shaab was in keeping with wide-impact-area ordnance dropped by fighter jets or drones. Images of strikes indicated bombs of up to 2,000 lbs (900 kg) had been dropped, he said.
Hezbollah, which frequently announces its own strikes, has occasionally used the short-range Burkan, with a warhead of up to 500 kgs (1,100 pounds). Many of the attacks it has announced have used weapons with far smaller warheads, such as guided anti-tank rockets that typically carry warheads of less than 10 kg.
"Hezbollah does have much ... heavier warheads on their ballistic missiles that have not been used yet," Krieg said.
Israel's military and Hezbollah did not respond to questions about ordnance.
Hezbollah's goal, Krieg said, was to drive out Israeli civilians.
"For that, Hezbollah doesn't need to cause massive structural damage to civilian areas or civilian buildings."