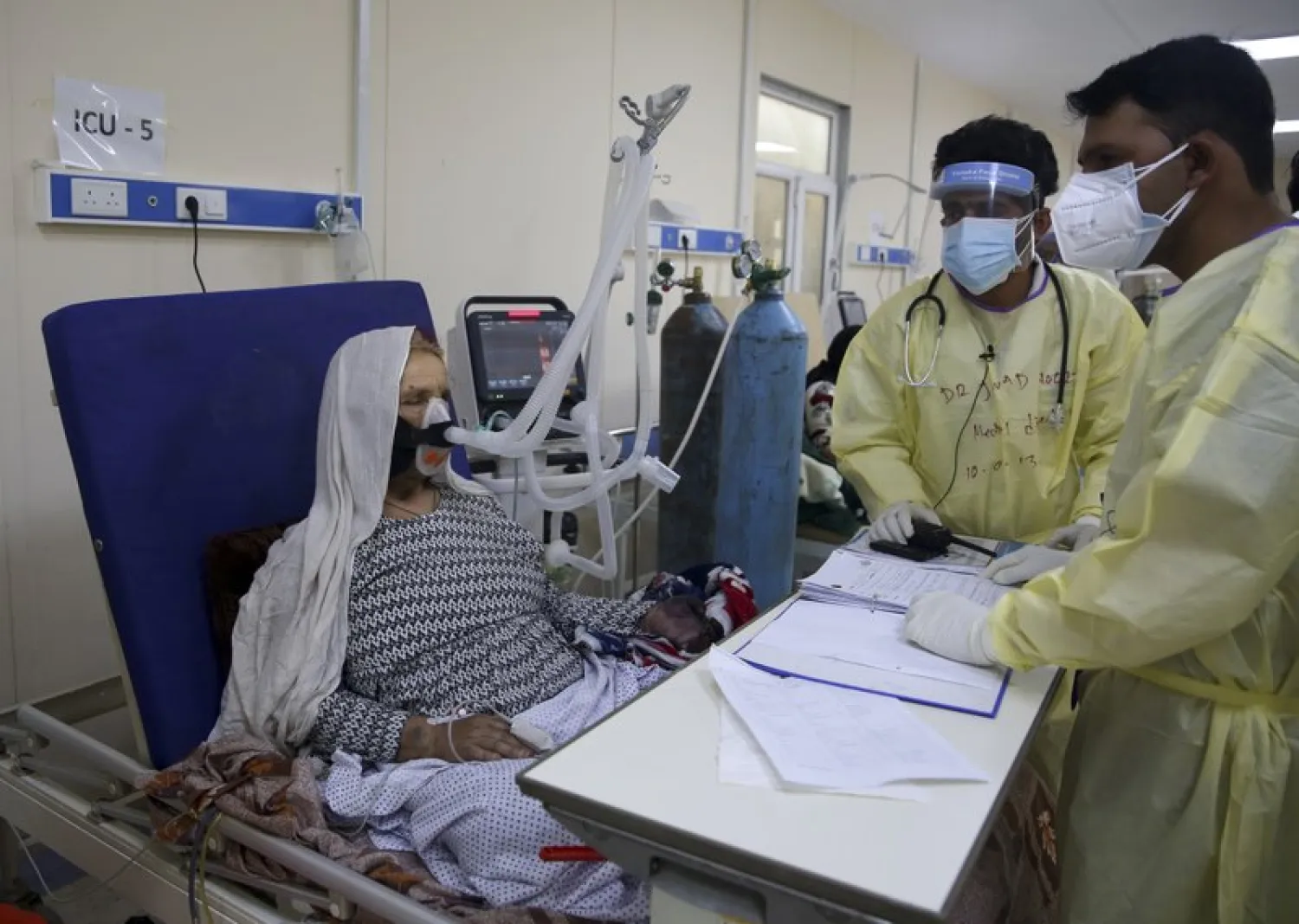
The intensive care unit at the Afghan capital's premier hospital for COVID-19 patients is a medical nightmare - and a stark warning how the country´s war-ravaged health care system risks collapsing.
Family members, without protective equipment and only a few wearing face masks, help care for the patients lying in hospital beds. They say they have no choice because there are not enough nurses and other medical staff.
The next-of-kin often guard their loved one´s oxygen tank, fearing it could be stolen because there is a shortage of just about everything, including oxygen cylinders.
The 100-bed Afghan-Japan Communicable Disease Hospital in western Kabul is one of only two facilities for coronavirus testing and treatment in the Afghan capital. Newly graduated Afghan doctors have joined the 370-member staff after many of the hospital's experienced physicians walked out a few months ago, fearing the virus.
The 92-square-meter (1,000-square-foot) ICU ward has only 13 beds, and COVID-19 patients admitted here are in critical condition; few are hooked up to ventilators, some of the others rely on oxygen tanks.
Assadullah, who like many Afghans goes by only one name, says he struggled to stay awake night after night at the ICU ward, guarding the tank that kept his father alive. In his father's final days, the relative of another patient came over, threatening to take the tank.
"Your father is dying but mine is alive, he told me ... in such a situation, how could I have left my father alone," said Assadullah, who lost his father to the virus on Tuesday.
Abdul Rahman, 42, feels the same way and rushes to rub his 70-year-old mother's back every time she coughs.
A few beds away, 64-year-old Mohammad Amin's left foot has turned black from gangrene that set in after a blood clot due to the virus. His son and wife tend to him as best they can, but they say it's exhausting.
For the hospital's director, Hakimullah Saleh, every staffer is a hero, risking their own life to provide critical care. They face so many work challenges, he said, on top of which they sometimes have to deal with "threats" from distraught families who feel the hospital is not doing enough.
One of Saleh's heroes, Dr. Jawad Norzai, is relentless in his devotion to the patients, he said. Along with his job as chief surgeon, Norzai visits over 60 patients a day and finds the time to train new doctors, Saleh said.
The 32-year-old Norzai got his medical diploma in 2013 and worked first for private hospitals, joining the Afghan-Japan only after hearing how many of the staff had left. Norzai said he, like many medical professionals, contracted the virus but recovered. He said he infected several of his family members but luckily, they also recovered.
Another one of the Afghan-Japan doctors who recovered from the virus is Mozhgan Nazehad, 35. "I spent three nights awake because of severe pain, back pain, and lower limb pain, that pain I will never forget," said Nazehad, who lives apart from her family to keep them safe.
The other hospital that treats COVID-19 patients is the Ali Jenah, funded by Pakistan, a 200-bed but less-equipped facility, also in western Kabul. There is also an isolation center in the dormitory of the Kabul University, but it does not provide treatment.
According to the Health Ministry, more than 1,700 medical workers - including 40 at the Afghan-Japan hospital - were infected while providing care to COVID-19 patients; 26 have died.
Afghanistan has so far recorded almost 35,000 cases of the virus, including 1,094 deaths, with the number of infections thought to far outnumber the official tally.
The International Rescue Committee warned last month that Afghanistan is on the brink of a humanitarian disaster because the government is unable to test some 80% of possible coronavirus cases.
The Health Ministry said it now has the capacity to test only 2,500 people per day. Last month, 10,000 to 20,000 people were coming daily, asking to be tested, but the government had to turn many down. Afghanistan has one doctor for every 3,500 people, less than a fifth of the global average, according to the World Health Organization.
The International Committee of the Red Cross said on Tuesday that in addition to the COVID-19 health crisis faced in Afghanistan, the socioeconomic impact of the virus could become catastrophic with 12.4 million people - one third of the country´s population - already considered to be living at "emergency" levels of food shortages.
Seemingly indicative of the fractured health care system, Afghan President Ashraf Ghani´s special envoy for economic development, Yosuf Ghaznafar, went to Turkey when he became ill with COVID-19. He died of the disease there in early July, according to a statement from the presidency - the most senior Afghan official so far to die of the virus.
"Your father is dying but mine is alive, he told me ... in such a situation, how could I have left my father alone," said Assadullah, who lost his father to the virus on Tuesday.
Abdul Rahman, 42, feels the same way and rushes to rub his 70-year-old mother's back every time she coughs.
A few beds away, 64-year-old Mohammad Amin's left foot has turned black from gangrene that set in after a blood clot due to the virus. His son and wife tend to him as best they can, but they say it's exhausting.
For the hospital's director, Hakimullah Saleh, every staffer is a hero, risking their own life to provide critical care. They face so many work challenges, he said, on top of which they sometimes have to deal with "threats" from distraught families who feel the hospital is not doing enough.
One of Saleh's heroes, Dr. Jawad Norzai, is relentless in his devotion to the patients, he said. Along with his job as chief surgeon, Norzai visits over 60 patients a day and finds the time to train new doctors, Saleh said.
The 32-year-old Norzai got his medical diploma in 2013 and worked first for private hospitals, joining the Afghan-Japan only after hearing how many of the staff had left. Norzai said he, like many medical professionals, contracted the virus but recovered. He said he infected several of his family members but luckily, they also recovered.
Another one of the Afghan-Japan doctors who recovered from the virus is Mozhgan Nazehad, 35. "I spent three nights awake because of severe pain, back pain, and lower limb pain, that pain I will never forget," said Nazehad, who lives apart from her family to keep them safe.
The other hospital that treats COVID-19 patients is the Ali Jenah, funded by Pakistan, a 200-bed but less-equipped facility, also in western Kabul. There is also an isolation center in the dormitory of the Kabul University, but it does not provide treatment.
According to the Health Ministry, more than 1,700 medical workers - including 40 at the Afghan-Japan hospital - were infected while providing care to COVID-19 patients; 26 have died.
Afghanistan has so far recorded almost 35,000 cases of the virus, including 1,094 deaths, with the number of infections thought to far outnumber the official tally.
The International Rescue Committee warned last month that Afghanistan is on the brink of a humanitarian disaster because the government is unable to test some 80% of possible coronavirus cases.
The Health Ministry said it now has the capacity to test only 2,500 people per day. Last month, 10,000 to 20,000 people were coming daily, asking to be tested, but the government had to turn many down. Afghanistan has one doctor for every 3,500 people, less than a fifth of the global average, according to the World Health Organization.
The International Committee of the Red Cross said on Tuesday that in addition to the COVID-19 health crisis faced in Afghanistan, the socioeconomic impact of the virus could become catastrophic with 12.4 million people - one third of the country´s population - already considered to be living at "emergency" levels of food shortages.
Seemingly indicative of the fractured health care system, Afghan President Ashraf Ghani´s special envoy for economic development, Yosuf Ghaznafar, went to Turkey when he became ill with COVID-19. He died of the disease there in early July, according to a statement from the presidency - the most senior Afghan official so far to die of the virus.