For decades, a deadly type of childhood cancer has eluded science’s best tools. Now doctors have made progress with an unusual treatment: Dripping millions of copies of a virus directly into kids’ brains to infect their tumors and spur an immune system attack.
A dozen children treated this way lived more than twice as long as similar patients have in the past, doctors reported Saturday at an American Association for Cancer Research conference and in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Although most of them eventually died of their disease, a few are alive and well several years after treatment -- something virtually unheard of in this situation.
“This is the first step, a critical step,” said the study’s leader, Dr. Gregory Friedman, a childhood cancer specialist at the University of Alabama at Birmingham.
“Our goal is to improve on this,” possibly by trying it when patients are first diagnosed or by combining it with other therapies to boost the immune system, he said. The patients in the study were given the experimental approach after they failed other treatments.
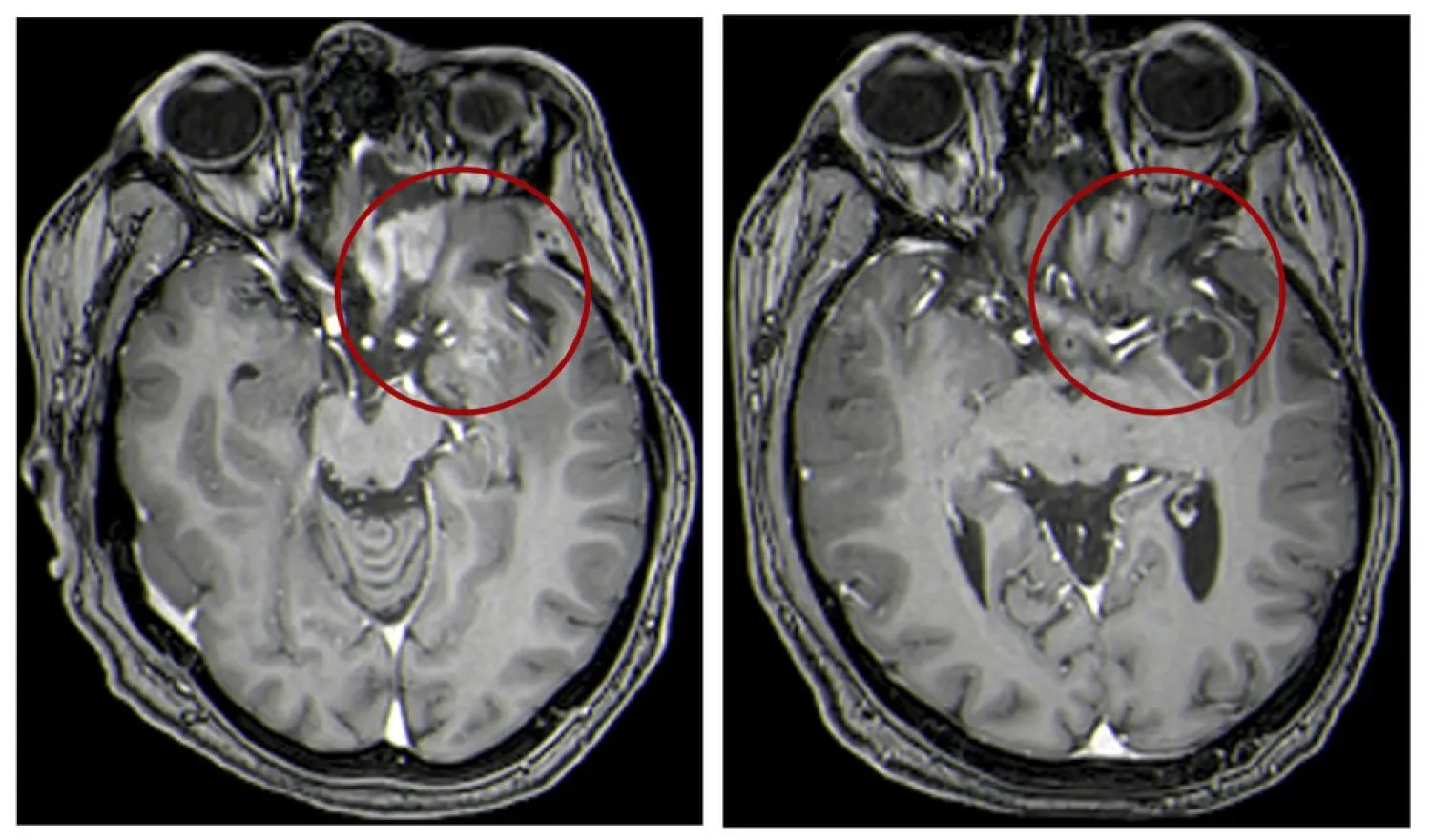
The study involved gliomas, which account for 8% to 10% of childhood brain tumors. They’re usually treated with surgery, chemotherapy or radiation but they often recur. Once they do, survival averages just under six months.
In such cases, the immune system has lost the ability to recognize and attack the cancer, so scientists have been seeking ways to make the tumor a fresh target. They turned to the herpes virus, which causes cold sores and spurs a strong immune system response. A suburban Philadelphia company called Treovir developed a treatment by genetically modifying the virus so it would infect only cancer cells.
Through tiny tubes inserted in the tumors, doctors gave the altered virus to 12 patients ages 7 to 18 whose cancer had worsened after usual treatments. Half also received one dose of radiation, which is thought to help the virus spread.
Eleven showed evidence in imaging tests or tissue samples that the treatment was working. Median survival was just over a year, more than double what’s been seen in the past. As of last June -- the cutoff for analyzing these results -- four were still alive at least 18 months after treatment.
Tests also showed high levels of specialized immune system cells in their tumors, suggesting the treatment had recruited the help needed from the body to attack the disease.
No serious safety issues were seen, though there were several procedure-related complications and mild side effects including nausea, vomiting, diarrhea and fatigue.
Jake Kestler had the treatment when he was 12.
“It went very well. He lived for a year and four months after that,” long enough to celebrate his bar mitzvah, go with his family to Hawaii and see a brother be born, said his father, Josh Kestler, a financial services executive from Livingston, New Jersey.
Jake died April 11, 2019, but “we have no regrets whatsoever” about trying the treatment, said Kestler, who with his wife has started a foundation, Trail Blazers for Kids, to further research.
“It’s a devastating disease for these patients and their families,” and the early results suggest the virus treatment is helping, but they need to be verified in a larger study, which doctors are planning, said Dr. Antoni Ribas, a cancer specialist at the University of California, Los Angeles, and president of the group holding the conference.
Friedman said studies are continuing in adults as well, and plans are in the works for other types of childhood brain tumors. US government grants and several foundations paid for the study, and several doctors have financial ties to Treovir.
Only one similar virus therapy is currently approved in the United States -- Imlygic, also a modified herpes virus, for treating melanoma, the most serious type of skin cancer.