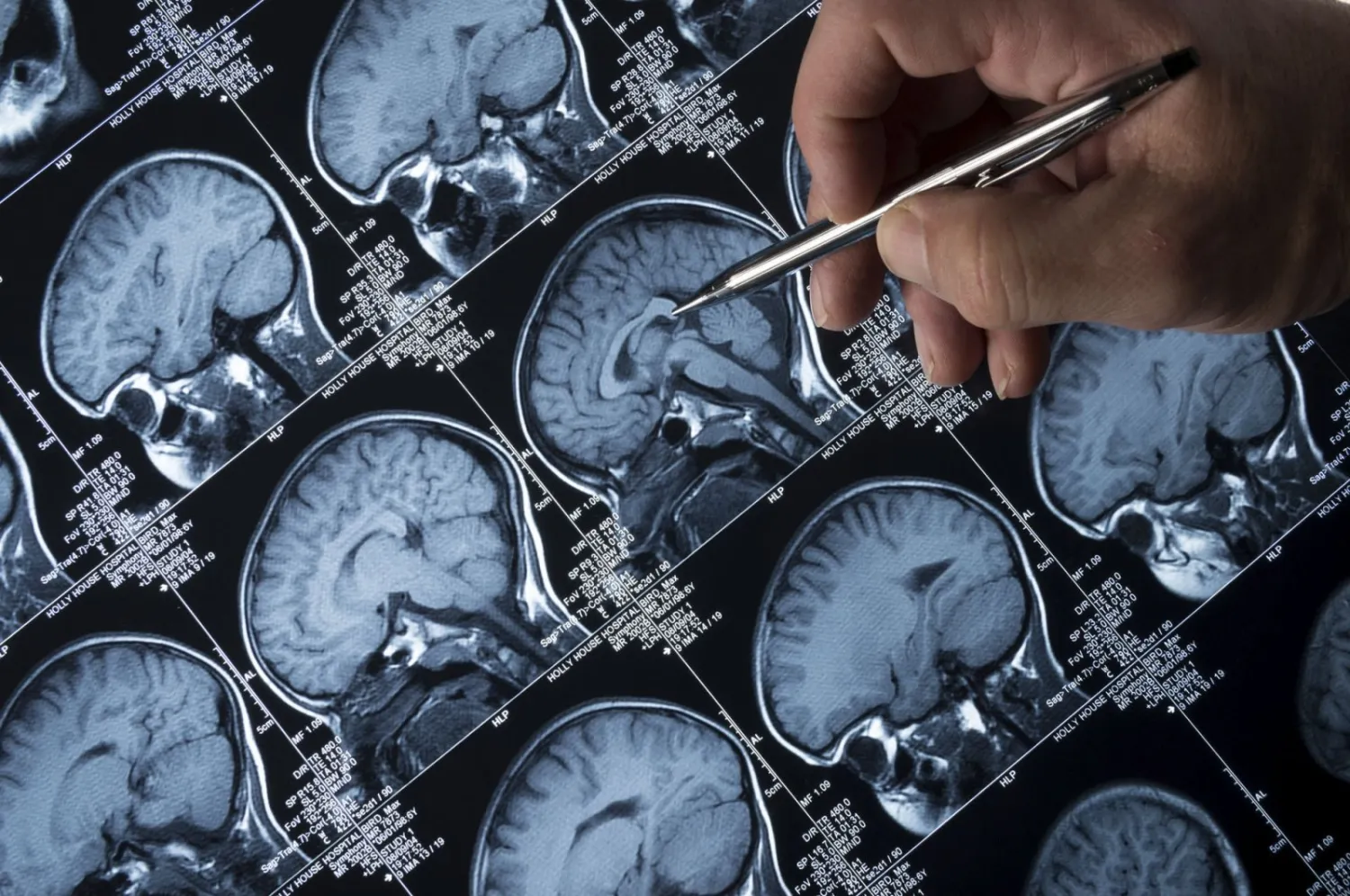
An international research team from the University of Michigan's Health Rogel Cancer Center found that Metformin, a drug commonly prescribed against diabetes, holds promise against a rare type of childhood brain tumor.
Posterior fossa ependymomas -- or PFAs affect neurons in the brain or the spinal cord, and can occur at any age, but often hit young children. Most cancers are known to arise from genetic mutations or errors, but PFAs lack such cancer-driving genetic mutations.
In the study published on October 5 in the journal Science Translational Medicine, the team found that the main reason behind the tumor in the disorder of two metabolic pathways that had been previously associated with DIPGs—glycolysis and the mitochondrial tricarboxylic acid cycle, a series of enzymes-driven chemical reactions that are vital for all living cells that use oxygen for respiration.
Diabetes treatment was an obvious field to turn to when looking for ways to suppress glucose metabolism -- the same process driving the PFA tumors. So, the researchers decided to see how a common diabetes drug, metformin, would affect PFA tumor cells.
"We found that metformin suppressed the cancer cells' metabolism and killed the cells in some PFA ependymoma tumors. And, unexpectedly, we found that metformin actually lowers EZHIP -- the protein that was causing these epigenetic changes in the first place," explained Sriram Venneti, professor at the department of pathology at Michigan Medicine, in a report posted on the university's website.
Meanwhile, when metformin was given to mice carrying patient-derived tumors, it lowered tumor metabolism, shrank the tumors and led to longer survival times in a subset of metformin-sensitive tumors.