A smiling physiotherapist beams in a framed photo inside the Red Cross center here, hinting at the radiant personality that charmed her orthopedic patients before a man with polio took out a gun hidden in his wheelchair and killed her.
The slaying of Lorena Enebral Perez at a clinic in the northern city of Mazar-e Sharif followed the roadside killing of six Afghans working for the International Committee of the Red Cross (ICRC) and three abductions in the past year, part of a spike in violence by smaller militias and by the terror group Taliban that has led to more than 200 deaths in the past week.
That violence has prompted the international aid agency to shut down two of its offices in the northern part of the country and to scale down operations in Mazar-e Sharif — a decision that will affect hundreds of thousands of Afghans who receive aid from the organization in seven northern provinces.
“The places where you have war and insecurity are the places where your help is needed,” said Alberto Cairo, a doctor who during the early 1990s spearheaded the creation of the ICRC’s orthopedic program, which treats 160,000 people annually across the country. “At the same time, you cannot deliver it. If we cannot guarantee the security of our staff, how can we work?”
So far this year, there have been 107 attacks on health facilities, up from 41 last year, according to the UN Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs. Fifteen aid workers have been killed in attacks, and an additional 43 have been abducted this year, down from 121 kidnappings the year before.
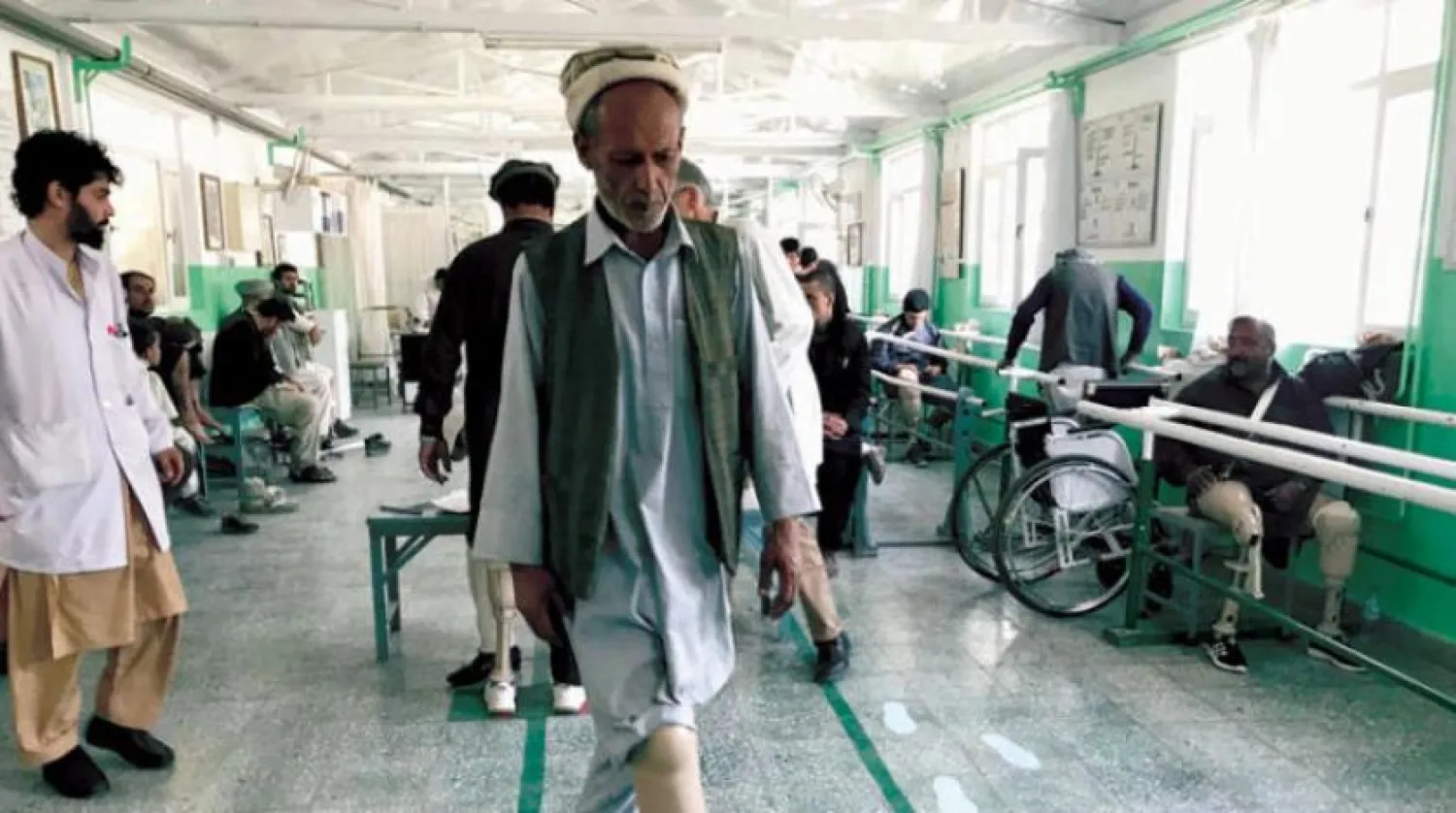
The orthopedic center’s roughly 8,500 patients who have lost legs to war or stray land mines, plus an additional 17,500 who have problems walking because of cerebral palsy, polio and other ailments, will still be able to receive treatment at the Mazar-e Sharif clinic. But the approximately 675,000 other Afghans who rely on the ICRC for food, water or medical aid in
the north will be left without options until the Afghan government or a different aid group fills the gap.
With US Secretary of State Rex Tillerson calling on Pakistan to help force the Taliban into peace negotiations amid a surge of 4,000 more U.S. troops, the militant group is fighting for a stronger presence outside its southern strongholds.
In that setting, more aid workers in areas once considered relatively safe have become targets for attacks or abductions. Meanwhile, more people need help.
In the past 12 months, 8,000 civilians have either died or been injured by military operations, down slightly from a peak of 8,500 in the previous year, according to the United Nations.
UN officials say humanitarian aid groups are trying to strike a balance by limiting their operations in some areas or prioritizing services to meet only the most urgent demands.
“We have to put the oxygen mask on ourselves before we can help others,” said Toby Lanzer, the UN humanitarian coordinator in Afghanistan. “I think, for the time being, you will see a reduction of aid in some of the areas where aid agencies have been hit.”
The erosion of security in the north has multiple causes, security analysts say.
In the hostile province of Kunduz, fighting between the Taliban and government forces has led to instability all around, making it harder for aid groups to know who is in charge. Elsewhere, smaller renegade groups — some of whom claim affiliation with ISIS — have taken hold in areas not under firm control of the government or the Taliban.
Those groups are behind many of the aid worker abductions and the attacks on medical facilities, said Obaid Ali, a director with the Afghan Analysts Network, who focuses on security issues in the north.
“They are small groups who work under their own flag, and in many cases, they refuse to obey Taliban rule and honor local culture,” Ali said. In the case of abductions, “it’s really hard, and it’s really dangerous to approach these people and discuss terms with them.
The increased instability revealed itself to the ICRC in December when a Spanish member of the staff was abducted by a group of gunmen while traveling from Kunduz to Mazar-e Sharif. The man was held for a month before the ICRC negotiated his release.
The Washington Post
Exclusive for Asharq Al-Awsat