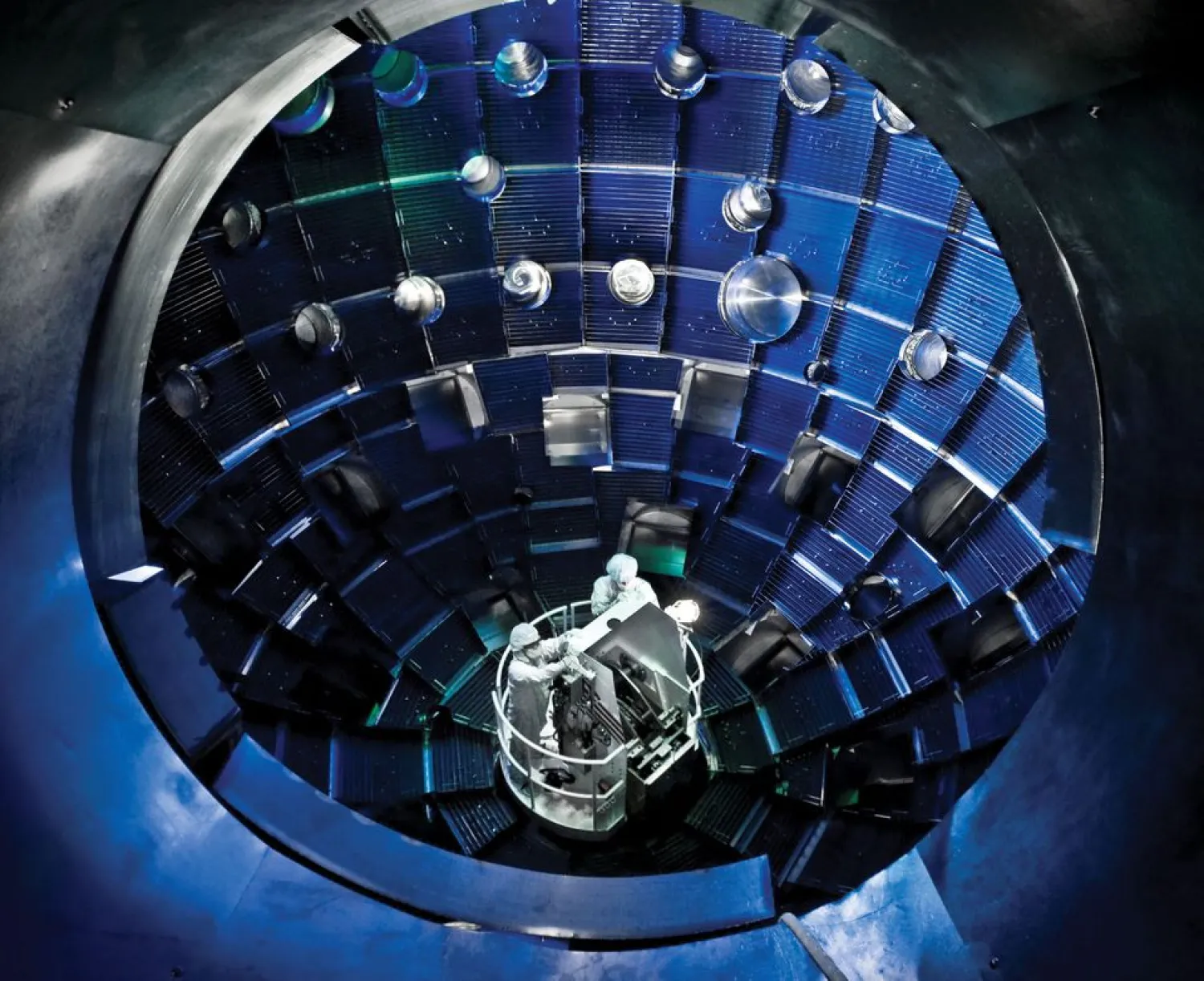
US government scientists said on Wednesday they have taken an important step in the long trek toward making nuclear fusion - the very process that powers stars - a viable energy source for humankind.
Using the world's largest laser, the researchers coaxed fusion fuel for the first time to heat itself beyond the heat they zapped into it, achieving a phenomenon called a burning plasma that marked a stride toward self-sustaining fusion energy.
The energy produced was modest - about the equivalent of nine nine-volt batteries of the kind that power smoke detectors and other small devices. But the experiments at a Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory facility in California represented a milestone in the decades-long quest to harness fusion energy, even as the researchers cautioned that years of more work are needed.
The experiments produced the self-heating of matter in a plasma state through nuclear fusion, which is the combining of atomic nuclei to release energy. Plasma is one of the various states of matter, alongside solid, liquid and gas.
"If you want to make a camp fire, you want to get the fire to hot enough that the wood can keep itself burning," said Alex Zylstra, an experimental physicist at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory - part of the US Energy Department - and lead author of the research published in the journal Nature.
"This is a good analogy for a burning plasma, where the fusion is now starting to become self-sustaining," Zylstra said.
The scientists directed 192 laser beams toward a small target containing a capsule less than a tenth of an inch (about 2 mm) in diameter filled with fusion fuel consisting of a plasma of deuterium and tritium - two isotopes, or forms, of hydrogen.
At very high temperatures, the nucleus of the deuterium and the nucleus of the tritium fuse, a neutron and a positively charged particle called an "alpha particle" - consisting of two protons and two neutrons - emerge, and energy is released.
"Fusion requires that we get the fuel incredibly hot in order for it to burn - like a regular fire, but for fusion we need about a hundred million degrees (Fahrenheit). For decades we've been able to cause fusion reactions to occur in experiments by putting a lot of heating into the fuel, but this isn't good enough to produce net energy from fusion," Zylstra said.
"Now, for the first time, fusion reactions occurring in the fuel provided most of the heating - so fusion is starting to dominate over the heating we did. This is a new regime called a burning plasma," Zylstra said.
Unlike burning fossil fuels or the fission process of existing nuclear power plants, fusion offers the prospect of abundant energy without pollution, radioactive waste or greenhouse gases. Nuclear fission energy comes from splitting atoms. Fusion energy comes from fusing atoms together, just like inside stars, including our sun.
Private-sector ventures - dozens of companies and institutions - also are pursuing a fusion energy future, with some oil companies even investing.
"Fusion energy is the holy grail of clean limitless energy," said Annie Kritcher of Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory, lead designer for the experiments conducted in 2020 and 2021 at the National Ignition Facility and first author of a companion paper published in the journal Nature Physics.
In these experiments, fusion produced about 10 times as much energy as went into heating the fuel, but less than 10% of the total amount of laser energy because the process remains inefficient, Zylstra said. The laser was used for only about 10 billionths of a second in each experiment, with fusion production lasting 100 trillionths of a second, Kritcher added.
Zylstra said he is encouraged by the progress.
"Making fusion a reality is an enormously complex technological challenge, and it will require serious investment and innovation to make it practical and economical," Zylstra said. "I view fusion as a decadal-scale challenge for it to be a viable source of energy."