President Donald Trump's administration has rebuffed efforts by Middle Eastern allies to start diplomatic negotiations aimed at ending the Iran war that started two weeks ago with a massive US-Israeli air assault, according to three sources familiar with the efforts.
Iran, for its part, has rejected the possibility of any ceasefire until US and Israeli strikes end, two senior Iranian sources told Reuters, adding that several countries had been trying to mediate an end to the conflict.
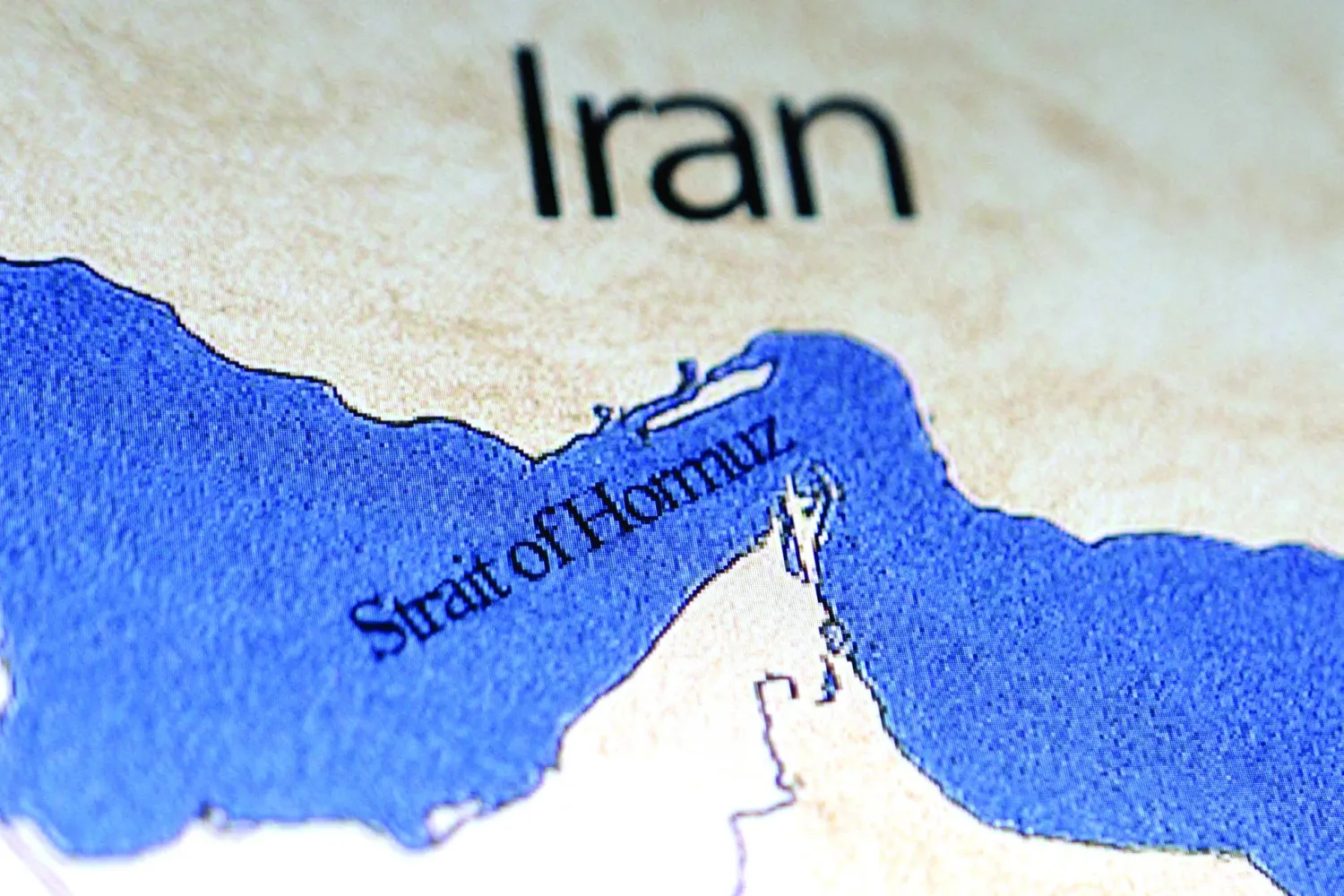
The lack of interest from Washington and Tehran suggests both sides are digging in for an extended conflict, even as the widening war inflicts civilian casualties and Iran's closure of the Strait of Hormuz sends oil prices soaring.
US strikes on Iran's Kharg Island, the country's main oil export hub, on Friday night underscored Trump's determination to press ahead with his military assault.
Iran's new Supreme Leader Mojtaba Khamenei has vowed to keep the Strait of Hormuz shut and threatened to step up attacks on neighboring countries.
The war has killed more than 2,000 people, mostly in Iran, and created the biggest-ever oil supply disruption as maritime traffic has halted in the Strait of Hormuz, through which a fifth of the world's oil is transported.
Oman, which mediated talks before the war, has tried multiple times to open a line of communication, but the White House has made clear it is not interested, according to two sources, who like others in this story were granted anonymity in order to speak freely about diplomatic matters.
A senior White House official confirmed Trump has rebuffed those efforts to start talks and is focused on pressing ahead with the war to further weaken Tehran's military capabilities.
"He's not interested in that right now, and we're going to continue with the mission unabated. Maybe there's a day, but not right now," the official said.
"President Trump said new potential leadership in Iran has indicated they want to talk and eventually will talk. For now, Operation Epic Fury continues unabated," a second senior White House official said when asked to comment on this story.
The Iranian sources said Tehran has rejected efforts by several countries to negotiate a ceasefire until the US and Israel end their airstrikes and meet Iran's demands, which include a permanent end to US and Israeli attacks and compensation as part of a ceasefire.
Egypt, which was involved in mediation before the war, has also tried to reopen communications, according to three security and diplomatic sources.
While the efforts do not appear to have made progress, they have secured some military restraint from neighboring countries hit by Iran, according to one of the sources.
Both the United States and Iran appear even less willing to engage than during the opening days of the war, when senior US officials reached out to Oman to discuss de-escalating, according to several sources.
One source said Iran's top security official, Ali Larijani, and Foreign Minister Abbas Araghchi had also sought to use Oman as a conduit for ceasefire discussions that would have involved US Vice President JD Vance.
But those discussions have not materialized.
Instead, Iran's position has hardened, said a third senior Iranian source.
"Whatever was communicated previously through the diplomatic channels is irrelevant now," said the source.
"The Guards strongly believe that if they lose control over the Strait of Hormuz, Iran will lose the war," the source added, referring to the Revolutionary Guard Corps.
"Therefore, the Guards will not accept any ceasefire, ceasefire talks, or diplomatic efforts, and Iran’s political leaders will not engage in such talks despite attempts by several countries."