The year 2025 brought no respite for Lebanese language editor and proofreader Hamida Al-Shaker. Before the year had run its course, her decades-long professional journey was abruptly cut short.
Nearly 60, Al-Shaker had never used artificial intelligence tools or held a conversation with ChatGPT, as millions now do. She was unaware that the technologies rapidly spreading across mobile phones and computers were already doing her job, faster and more efficiently than any human could.
That quiet technological advance proved devastating. A sweeping transformation in the labor market became a tsunami, pushing Al-Shaker and millions of workers worldwide toward unemployment, sparing no sector and few age groups. The impact has been particularly harsh on employees over 50 who failed to keep pace with the accelerating speed of technological change.
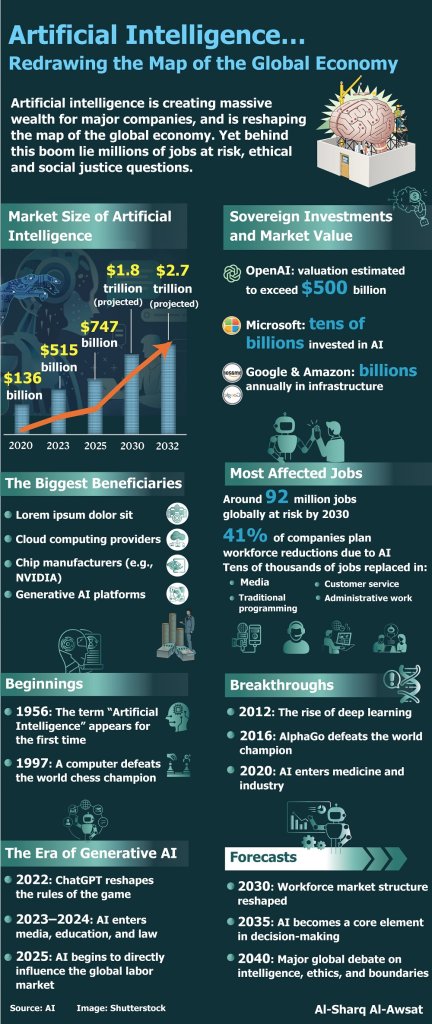
According to the website allaboutai, the adoption of artificial intelligence has already contributed to the loss of around 14 million jobs globally. And the wave is far from over. As many as 92 million jobs could disappear worldwide over the next five years.
At its core, artificial intelligence enables computer systems to mimic human thinking, make decisions, and execute complex tasks, from planning to practical application, particularly in editorial and knowledge-based work.
Shock and an uncertain future
Al-Shaker was unaware of this reality, a fact that led to a shock, followed by another, during 2025, which saw the widest spread yet of AI applications. The first shock came when she received a call from the human resources department informing her that her salary would be cut by 50 percent due to “financial difficulties facing the company.” Less than five months later, a second call informed her that she was being laid off, without explanation.
According to Al-Shaker, citing her department head, she was not alone. Half of the team lost their jobs due to the impact of artificial intelligence on client contracts, as companies increasingly turned to AI to draft their news, statements, and reports, either for free or at minimal monthly subscription costs, compared with the sums they previously paid to public relations and advertising agencies.
In this context, economic analyses published by Reuters indicate that annual subscriptions to advanced AI tools, even at the enterprise level, often do not exceed the cost of paying a single employee’s salary for a limited number of months. From a purely managerial perspective, this makes such decisions easy to justify financially.
As a result, Al-Shaker and her colleagues became just another figure in a cold equation. Companies boost profits and cut production costs, while growing numbers of workers are pushed out of the labor market, not because they lack competence, but because algorithms are cheaper than people.
Most affected sectors
Al-Shaker’s story is not an isolated case. It is part of a growing global phenomenon affecting workers across multiple sectors. Specialized reports indicate that jobs based on routine tasks or repetitive data processing are most vulnerable, as automation and generative AI tools expand. Among the most affected sectors are:
Customer service and call centers, where intelligent chat systems and text and voice analysis tools can now handle user inquiries with high efficiency, according to TechRT.
Data and administrative support tasks, such as data entry, file classification, and secretarial work, are being replaced by advanced automation tools, according to Complete AI Training.
Retail and supply chains, where self-checkout systems, smart warehouses, and inventory automation have reduced the need for cashiers and traditional warehouse workers, according to Pleeq Software and ninjatech.blog.
Manufacturing and production, where the spread of robots and automated control systems has intensified the impact of AI on manual labor jobs, according to All About AI.
Accounting and financial operations, where demand for basic roles has declined due to reliance on intelligent financial software capable of handling bookkeeping and routine processes, according to Complete AI Training.
Content creation and media, which have not been spared, are now threatened as AI is capable of writing, summarizing, and rewriting content, posing a challenge to a range of basic writing tasks.
Many workers who lost their jobs do not realize that they are victims of the so-called Fourth Industrial Revolution, which Klaus Schwab, founder and executive chairman of the World Economic Forum at the time, warned about years earlier.
Speaking at the World Government Summit in Dubai in 2016, Schwab said the world was “on the brink of a technological revolution that will fundamentally alter the way we live, work, and relate to one another.”
He added that the scale, scope, and complexity of the changes would be unprecedented, and that while their exact shape remained unclear, the response would have to be integrated and comprehensive across the public and private sectors, academia, and civil society.
Market demands and human skills
Much of what Schwab predicted has now come to pass, particularly in recent months, as companies worldwide accelerate their adoption of AI tools. Experience alone is no longer enough to remain competitive in the labor market. Traditional jobs are changing rapidly, and the required human skills have become more specialized and complex, with greater emphasis on working alongside intelligent systems and turning information into added value.
Professionals who understand how to integrate AI tools into their daily work without sacrificing quality or analytical depth are increasingly in demand, according to Maziad Hijaz, Editor-in-Chief at Hewar Group in Riyadh.
Hijaz told Asharq Al-Awsat that artificial intelligence has become an essential part of daily work in terms of speed and volume, while review, editing, and analysis remain entirely human responsibilities to ensure quality.
He added that the sector now requires new skills, and those who fail to adapt will be left behind. These include utilizing AI tools for writing and analysis, developing data literacy, employing predictive analysis, and transforming information into compelling narratives. Combining human skills with AI tools is what ensures excellence.
Firas Barakat, a strategic communications expert in Saudi Arabia, said AI represents a pivotal turning point in labor markets, enhancing efficiency while reshaping the nature of jobs and required skills.
Speaking to Asharq Al-Awsat, Barakat said AI has undoubtedly caused the loss of traditional roles involving routine tasks, but at the same time, it is a major engine for generating new jobs in advanced fields such as data analysis, cybersecurity, smart systems management, and digital solutions engineering, roles that did not exist just a few years ago.
History repeats itself
Technology expert Hassan Yahya, based in the United States, offered a historical perspective. He said this is not the first time the world has been stunned by technological advances, noting that similar fears over job losses have accompanied every major innovation.
He pointed to 1959, when General Motors introduced the industrial robot Unimate, triggering widespread warnings about threats to employment.
Yahya said that AI is already affecting millions of jobs, with projections from the World Economic Forum indicating that 92 million jobs will disappear over the next five years. However, more than 170 million new jobs are expected to be created, meaning a fundamental transformation of work rather than mass unemployment.
He added that eliminating jobs without replacing them does not serve companies or economies, making the creation of new roles inevitable. However, this requires learning how to work with AI, as ignoring the shift could leave many people outside a rapidly changing labor market.
Cost-cutting and profit maximization
The experiences of employees cannot be separated from a recurring economic equation that is evident in thousands of companies worldwide. Instead of retaining experienced staff with associated salaries, insurance, and end-of-service benefits, many firms are opting to replace them with AI.
A World Economic Forum report found that 41 percent of global companies plan to reduce their workforce by 2030 due to increased reliance on AI and automation.
Hijaz said AI adoption has also reshaped relationships with clients, accelerating work and significantly improving quality. He cited a Deloitte study showing that integrating AI into public relations reduced content production time by 25 to 35 percent while improving accuracy.
A market worth billions
The gains are split between business owners and AI companies, whose financial returns contrast sharply with the reality faced by thousands of displaced workers. In mid-2025, a Reuters report stated that OpenAI, the developer of ChatGPT, had reached annual revenues of around $10 billion by the end of the first half of the year, on track to exceed $12.7 billion by year's end, driven by surging demand for its services.
This growth is not limited to OpenAI. A Forbes report showed that other global technology companies with AI divisions are generating billions of dollars in additional annual revenue, making AI one of the most important profit sources for major tech firms, even as some lay off staff to improve cost efficiency.
Key players
The main players in the sector include OpenAI, best known for ChatGPT and a leader in large language models, with a strategic partnership with Microsoft.
Google DeepMind follows, having developed powerful models such as Gemini and AlphaGo, and leading in scientific, medical, and research-oriented AI.
Microsoft itself has become a global force in AI, investing billions in OpenAI and integrating AI across Windows, Office through Copilot, and Azure AI.
NVIDIA focuses on developing the chips and processors that power AI, while Meta offers open-source models such as LLaMA. Amazon Web Services leads in cloud-based AI, and Anthropic has emerged as a strong competitor in the field of language models.
The global AI market was estimated at around $747.9 billion in 2025 and is projected to grow to $2.74 trillion by 2032, according to AffMaven.
Concerns over consequences
The stark contrast between multibillion-dollar AI revenues and the growing risk facing millions of workers raises a central ethical and economic question. Why do companies benefit from technology to cut costs and boost profits while often postponing or ignoring their social responsibility toward displaced employees?
Economists warn that such savings are frequently achieved without genuine retraining efforts or alternative job creation, deepening global unemployment rather than addressing it.
Islam Al-Shafii, an economist based in New York, cited remarks by US Federal Reserve Chair Jerome Powell on Dec. 20, warning of waves of layoffs linked to AI or companies halting job postings for the same reason.
Al-Shafii said the current fear of AI remains precautionary, as it has not yet fully replaced humans. The real risk, he said, is that work previously requiring five employees can now be done by one person using AI.
He added that while some professions remain relatively safe for now, such as skilled trades, concerns persist over safety and decision-making, with international organizations expressing reservations.
Breaking monopolies
Yahya argued that confronting these changes requires breaking three major monopolies: the monopoly of university degrees in hiring, as companies like Google and Dell focus on skills rather than diplomas; the technological monopoly, as AI empowers individuals to execute ideas without large teams; and the language monopoly, as AI allows interaction in native languages, opening the digital economy to millions.
The digital economy is expected to exceed $24 trillion by 2025, accounting for approximately 21 percent of the global economy and growing faster than traditional sectors.
Capitalism under strain
Al-Shafii warned that advanced capitalist societies, which rely heavily on tax revenues from employees, could face systemic strain if jobs are replaced by AI. Without a sufficient tax base, governments may struggle to fund essential services, which can potentially lead to social instability and collapse.
He noted that business owners who once built factories in East Asia for cheap labor are now returning home to rely on robots for production.
United Nations concern
The issue has also reached the United Nations, particularly at its headquarters in New York. Al-Shafii stated that there is a deep concern over AI, but institutions often focus on gains while overlooking the associated losses.
He noted that AI supports many sustainable development goals and cybersecurity efforts, but its negative aspects, including cyber fraud and surveillance risks, have yet to be fully addressed. UN Secretary-General Antonio Guterres has repeatedly warned against militarizing AI and entrusting humanity’s future to algorithms.
Threat or opportunity?
Concerns over AI extend beyond job losses to issues of transparency and information security. Hijaz said AI requires greater responsibility to ensure accuracy and disclosure.
Asked whether AI is a threat or an opportunity, he said it is an inevitable development that must be harnessed. Like the computer and the internet before it, initial fears will likely give way to empowerment.
He added that creativity remains a uniquely human value that AI cannot replace, and that technology enhances rather than eliminates it.
Not a replacement
Translation professor Mohammed Khair Nadman told Asharq Al-Awsat that AI tools now save around 60 percent of time in translation and writing, supporting but not fully replacing human work. He warned that AI can still make serious errors, making human oversight essential.
M. A. Hadi, MD, Head of the Department of Pathology at a hospital in the United States, said that the current wave of misinformation fueled by easy access to online medical content and artificial intelligence "will not last long if simple regulations are put in place".
He explained that reading medical information online or collecting data through AI does not make someone a physician, just as reading news does not make a journalist, nor learning about car engines makes one a mechanic. "In the same way," he noted, "having extensive legal knowledge through AI does not qualify someone to be accepted in court as a lawyer."
Dr. Hadi added that while such knowledge can empower individuals to ask better and more informed questions, it does not replace professional expertise. "AI can help people engage more effectively with professionals and may even push experts to become more transparent and ethical, reducing the space for fraud, middlemen, and bad practices," he said.
Quoting the Arabic proverb "give your bread to the baker, even if he eats half of it", Dr. Hadi stressed that while the "do-it-yourself" mindset has always existed and can be useful, real work must still be done by qualified experts. "Artificial intelligence will likely make professionals better, as general knowledge continues to expand," he said, "but professional training, experience, and licensing cannot and should not be granted to laypeople, even if they are well-read or AI-assisted."
He warned that partial or incomplete knowledge can be more harmful than helpful when applied in practice, concluding that, ultimately, "the evidence is in the results."
A final attempt
Al-Shaker, living in crisis-hit Lebanon without a private sector pension system, believed her regional company job was secure. After losing it, she tried to catch up, creating a LinkedIn account, registering on job platforms, taking free online courses, and sending dozens of resumes, often receiving automated or no responses.
Her story reflects the dilemma of an entire generation pushed out of the market, not due to lack of competence, but because the rules changed abruptly.
She ended with a bitter question: Nearly two centuries after the Industrial Revolution sparked the call, “Workers of the world, unite,” will there now be a call saying, “Employees of the world, unite?”









