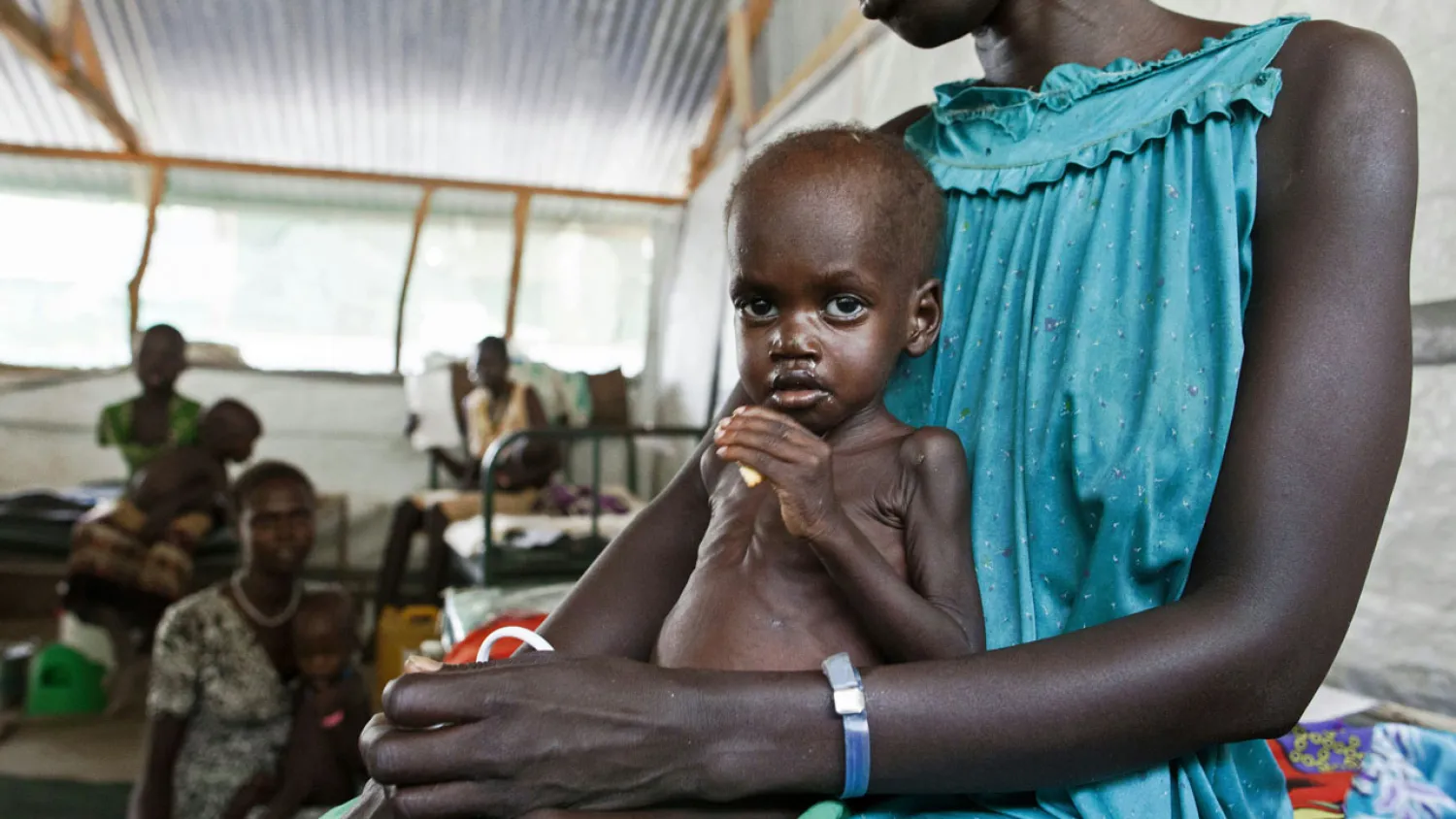
A major study published over the weekend said almost every country in the world has serious nutrition problems, either due to over-eating, leading to obesity or a lack of food, leading to undernutrition.
Researchers behind the Global Nutrition Report, which looked at 140 countries, said the problems were “stressing human development as a whole” and called for a critical change in the response to this global health threat.
The report found that while malnutrition rates are falling globally, their rate of decline is not fast enough to meet the internationally agreed Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) to end all forms of malnutrition by 2030.
It said that more than 155 million children aged under five are stunted due to lack of nutrition, and 52 million are defined as “wasted”, meaning they do not weigh enough for their height, the report said.
At the other end of the spectrum, over-eating is taking a heavy toll on people of all ages worldwide: The report found that two billion of the world’s seven billion people are now overweight or obese.
In North America, a third of all men and women are obese.
Worldwide, at least 41 million children under five are overweight, and in Africa alone, some 10 million children are now classified as overweight.
Jessica Fanzo, a professor at Johns Hopkins University in the United States who co-led the report, said that historically, maternal anemia and child undernutrition have been seen as separate problems to obesity and non-communicable diseases.
Fanzo added that the reality is they are intimately connected and driven by inequalities everywhere in the world. That’s why governments need to tackle them holistically, not as distinct problems.
The report showed that funding for nutrition rose by just 2 percent to $867 million in 2015. It said funding needs to be “turbo charged” and called for a tripling of global investment in nutrition to $70 billion over 10 years.
The Global Nutrition Report is an independently produced annual analysis of the state of the world’s nutrition. It tracks progress on targets for maternal, infant and young child nutrition and on diet-related chronic diseases adopted by World Health Organization member states.