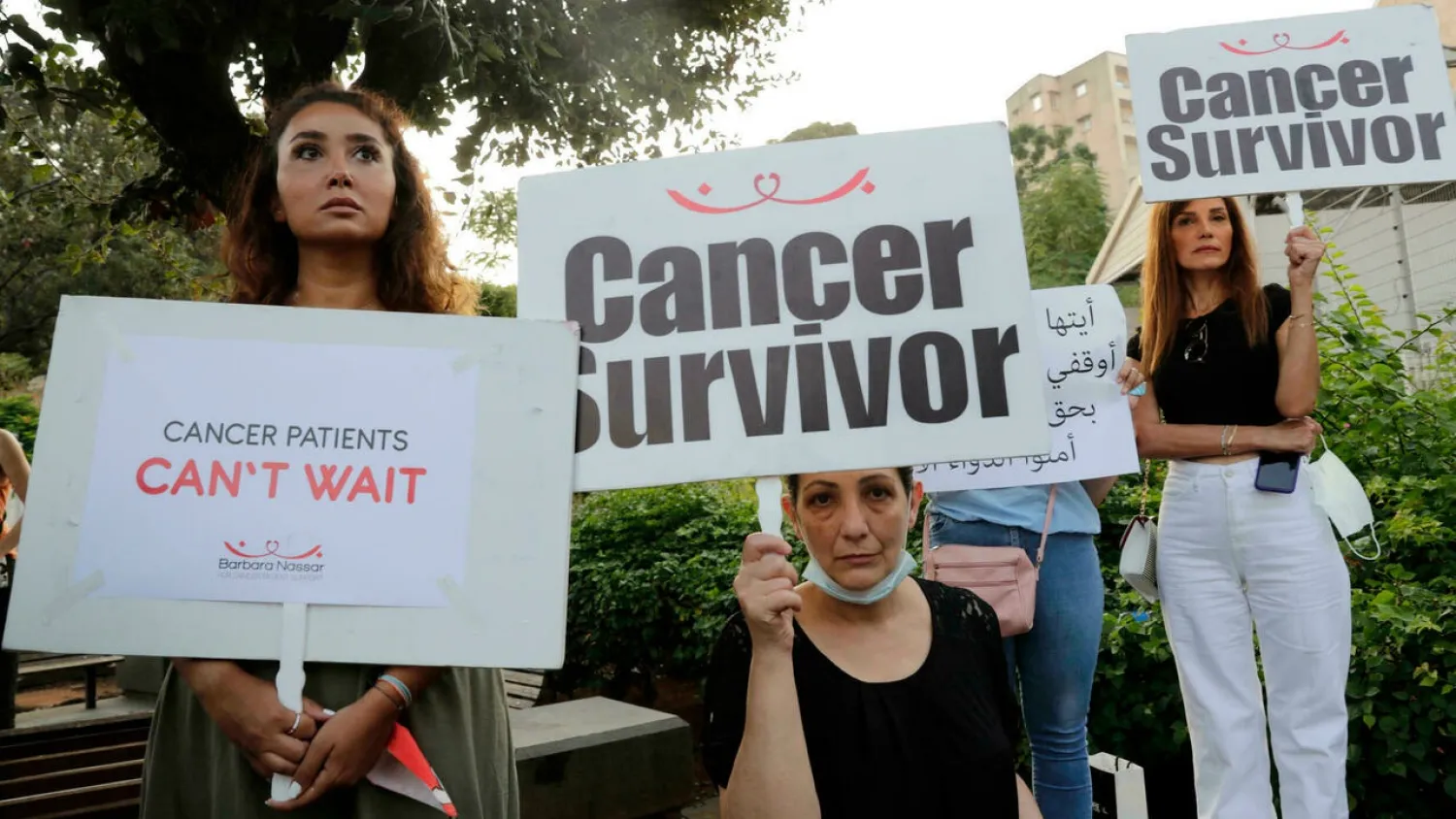As if her cancer treatment was not already agonizing enough, Rita is now wracked with worry about the medication she needs as Lebanon’s crippling economic crisis sparks drug shortages.
“The treatment is like fire shooting through your body,” the 53-year-old patient told AFP, asking that her real name not be given. “But now on top of that, we have to go hunting for the drugs.”
Lebanon is in the throes of one of the world’s worst economic crises since the mid-19th century, which has sparked a flurry of shortages from medicines to fuel as foreign currency reserves run low.
The health ministry has previously provided cancer medication at very low cost to patients without health insurance, but the patients say there are now almost no drugs to be found.
The shortages are threatening the treatment of tens of thousands of people, many of whom have taken to social media in a desperate plea to source the drugs they require.
Since Rita was diagnosed with uterine cancer three years ago, the disease has also spread to her lungs.
“My brother couldn’t find the drugs from the ministry,” said the single mother of three, her face etched with worry at his home in Kfar Nabakh in the Chouf mountains.
For now, she has borrowed money to buy the medicine at a much higher price on the black market. But she says she will not be able to afford to do this for long.
“What am I supposed to do? Sit around waiting for my turn?” she asked. “If you can’t find the drugs, you die.”
‘No drugs left’
The World Health Organization says 28,764 people have been diagnosed with cancer in Lebanon over the past five years, out of a total population of six million.
But doctors say the number of patients undergoing treatment is likely to be much higher.
The head of the Lebanese Society of Hematology and Blood Transfusion, Ahmad Ibrahim, said that around 2,500 new cases of leukemia and lymphoma are recorded each year in the Mediterranean country.
“Very little medication is left for their treatment,” he said. “Yet if they don’t follow regular treatment, some will die.”
Cancer drugs are just the latest medication to become scarce, with even painkillers disappearing from pharmacy shelves in recent months.
“Some have neared the end of their treatment and are about to get better, but now suddenly there are no more drugs left,” Ibrahim added.
This summer many Lebanese expats who return home have flown in with suitcases packed to the brim with boxes of medication for their loved ones.
Some drugs are available at a higher price on the black market, but in a country where three quarters of the population live in poverty, many cannot afford them.
Last month, importers said supplies of hundreds of kinds of drugs had run out, as the central bank owed millions of dollars to their suppliers abroad.
The authorities in turn accused importers of hoarding medicines with the aim of selling them later at a higher price, and blamed smuggling abroad for part of the problem.
‘They don’t care’
Many Lebanese see the lack of medicine as merely the latest outcome of decades of mismanagement of the country by a political class they say is selfish and corrupt.
The Barbara Nassar Association for Cancer Patient Support on Thursday staged a protest to demand better access to cancer medication.
“Can you believe it? In Lebanon, cancer patients -- with all their worries -- are forced to go down into the street and protest to demand medicine,” said its president, Hani Nassar.
“How is it the patient’s fault if the state is incapable of containing the crisis?”
In the Hazmieh suburb of Beirut, Patricia Nassif, 29, said she was afraid she would not be able to finish her breast cancer treatment.
She had been married for only eight months when she discovered in April that she had breast cancer, upending her dream to start a family when all of her friends were becoming pregnant.
“I often lose hope,” she said, wearing a black wig with a purple streak to match her outfit of black T-shirt and jeans.
She has finished a round of chemotherapy, but now fears she will have to spend thousands of dollars buying medication abroad for the next stage of her treatment.
“It’s humiliating,” she said, and accused the ruling class of doing little to help.
“It’s as if they were telling us: ‘Die slowly’. They don’t care about us.”