New Zealand ’s annual bird election is contested by cheeky parrots, sweet songbirds and cute, puffball robins. This year’s winner was a mysterious falcon that wouldn’t think twice about eating them.
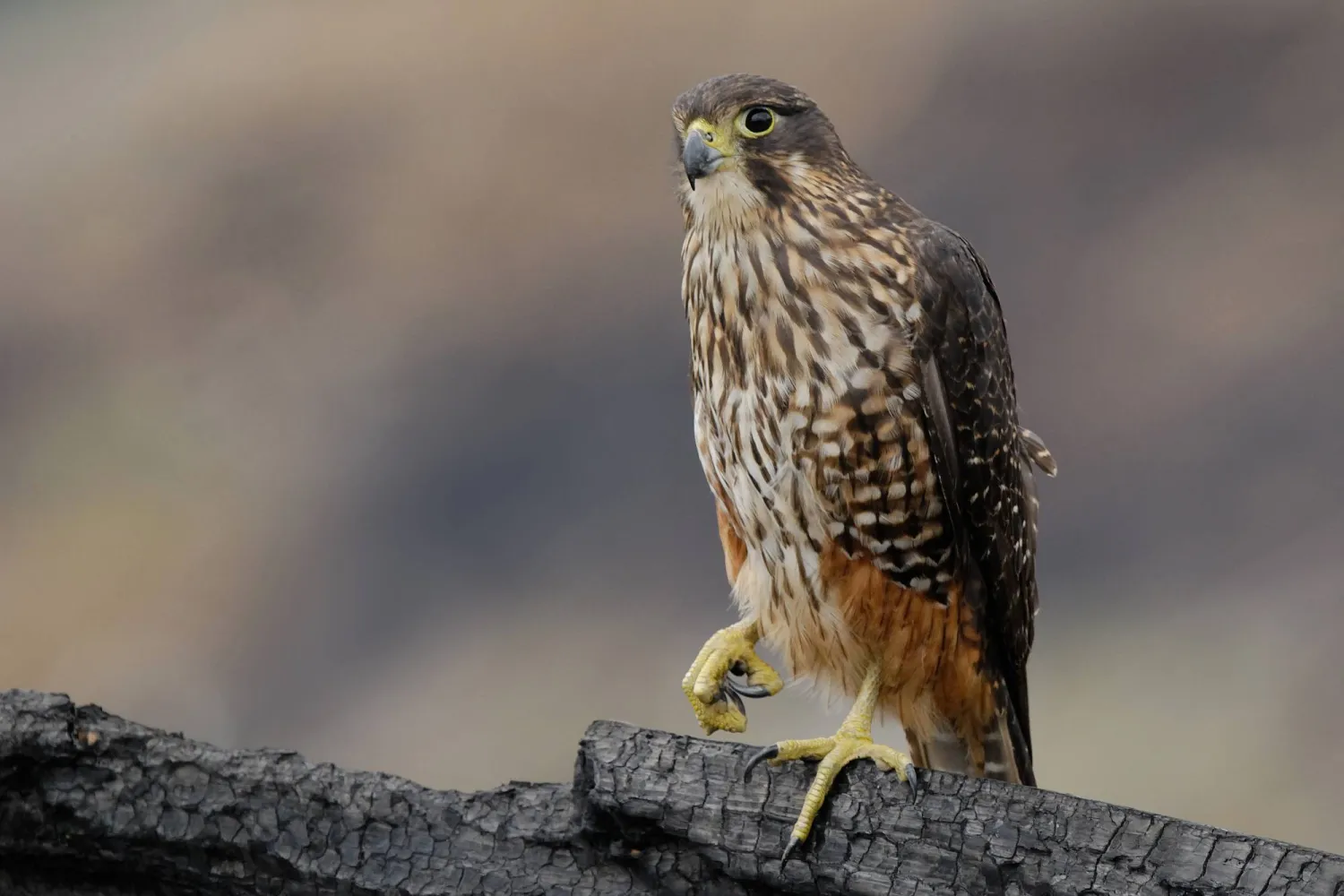
Kārearea, the Indigenous Māori name for the New Zealand falcon, was crowned Bird of the Year on Monday. But the annual poll, run by conservation group Forest & Bird, is no ordinary online vote.
The fiercely fought election sees volunteer (human) campaign managers apply to stump for their favorite bird. Feathers fly as avian enthusiasts seek to sway the public through meme battles, trash-talking poster campaigns and dance routines performed in bird costumes.
“Bird of the Year has grown from a simple email poll in 2005 to a hotly contested cultural moment,” said Forest & Bird Chief Executive Nicola Toki. “Behind the memes and mayhem is a serious message.”
The contest draws attention to New Zealand’s native bird species, with 80% designated as being in trouble to some degree. But it attracts passionate fandom because New Zealanders are bird-obsessed.
In a country with no native land mammals except for two species of bat, birds reign supreme. They appear in art, on jewelry, in schoolchildren’s songs, and in the name New Zealanders are known by abroad, “kiwis.”
Beloved birds include alpine parrots that harass tourists and pigeons which get so drunk on berries that they sometimes fall out of trees.
“This is not a land of lions, tigers and bears,” said Toki. “The birds here are weird and wonderful and not what you would expect to see perhaps in other countries.”
The first contest two decades ago attracted fewer than 900 votes. More than 75,000 people in the country of 5 million cast ballots this year.
It was the highest-ever voter turnout apart from an episode when Last Week Tonight host John Oliver volunteered as a campaign manager in 2023, prompting mostly joking accusations from New Zealanders of American interference. Perhaps inevitably, Oliver’s bird, the pūteketeke or Australasian crested grebe, won in a 290,000-vote landslide.
Other controversies have struck the poll. In 2021, there was mild uproar when a bat won the title, despite not being a bird.
The vote was ruffled by a foreign influence scandal in 2018 when self-styled comedians in Australia cast hundreds of fraudulent votes for a bird that shares its name with an Antipodean slang term for sex. Voters must now verify the email addresses used to cast their votes.
Forest & Bird said 87% of the votes in this year’s poll came from New Zealand. The falcon’s more than 14,500 votes appeared to have been won fair and square.
The majestic kārearea can fly at speeds of more than 200 km (124 miles) per hour and swoops to capture its prey, often smaller birds. The endemic species is threatened in New Zealand, vulnerable to electrocution on wires and loss of their forest habitats.
“They’re a mysterious bird and that’s partly because they’re cryptic, they’re often well-hidden,” said Phil Bradfield, a trustee of Kārearea Falcon Trust in Marlborough, on New Zealand’s South Island.
Official figures suggest between 5,000 and 8,000 New Zealand falcons remaining, although the true number is unknown. Bradfield said the “fast and sneaky and very special” raptor was a deserving Bird of the Year winner.
Other campaigns knew victory on Monday would take a miracle. Birds that are ugly — but not ugly enough to be funny — unknown or perceived as boring face an uphill slog.
That doesn’t deter bird lovers. The year 2025 was the first that all 73 bird competitors attracted campaign managers, with some electing to stump for contenders they knew would lose.
One was Marc Daalder whose scrappy, grassroots campaign for the tākapu, or Australasian gannet, drew 962 votes — about a 15th of the falcon’s.
“Running a campaign for one of the less popular birds is a more satisfying experience because you know the votes your bird received are a result of your hard work,” said Daalder, who is a (human) political journalist and three-time (bird) campaign manager.
Despite the near-record voter turnout, Toki from Forest & Bird said she feared New Zealanders would give up on some of the most threatened species as they grew more costly to protect, particularly from predators such as cats, rats and stoats.
“Successive governments in New Zealand have cumulatively reduced investment in conservation, which is the cornerstone of New Zealand’s economic prosperity,” she said, referring to tourism campaigns promoting the country’s scenic landscapes.
“People come here to see our native birds and the places they live in,” she said. “They’re not coming here to see shopping malls.”