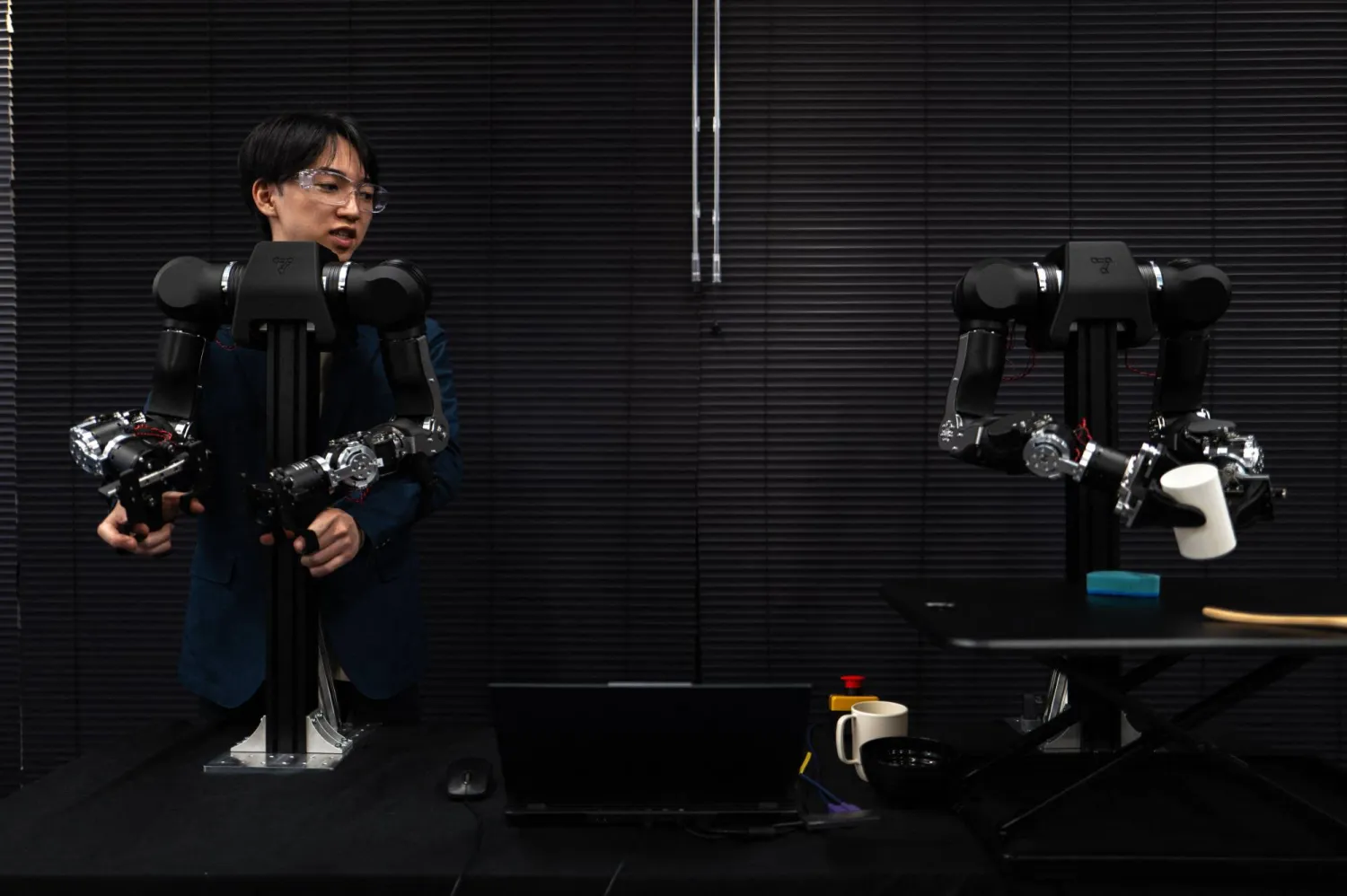
A pair of swiveling, human-like robotic arms, built for physical artificial intelligence research, mirror the motions of an operator in a VR headset twirling his hands like a magician.
With enough practice, arms like these can complete everyday tasks alone, claims Tokyo company Enactic, which is developing humanoid robots to wash dishes and do laundry in short-staffed Japanese care homes.
Welcome to the future of AI as it starts to infiltrate the material world in the form of smart robots, self-driving cars and other autonomous machines.
"The next wave of AI is physical AI," Jensen Huang, head of US chip giant Nvidia, said last year.
That's "AI that understands the laws of physics, AI that can work among us" and understands "how to perceive the world", Huang added.
Tech firms are pouring massive sums into physical AI, and Morgan Stanley predicts the world could have more than a billion humanoid robots by 2050.
The buzz is only heightened by videos showing advanced androids, often Chinese-made, dancing to Taylor Swift or pulling heavy objects with ease.
Beyond the promise of sci-fi robot butlers, the race has sparked concern over job losses, privacy and how long these innovations will take to actually be useful.
Hiro Yamamoto is the 24-year-old CEO of Enactic, whose OpenArm physical AI training devices are used by Nvidia and at top universities such as Stanford.
He plans to begin deploying new robots, currently under development, from next summer to "live alongside people in environments that are very chaotic, and where conditions are always changing" like care homes.
"So it has to be safe," with a soft exterior that won't injure anyone, Yamamoto said.
In the Chinese city of Guangzhou, a female figure with a glowing oval-shaped visor for a face, clad in white woven fabric like a fencing athlete, walked slowly across a stage last week to cheers and whispers.
It was the latest humanoid robot to be unveiled by Chinese electric vehicle maker XPeng, which is also pushing into physical AI.
Nimble machines made by US companies, such as Boston Dynamics' dog-like robots, have grabbed headlines over the years.
But government support and strong domestic supply chains are helping Chinese rivals, also including Unitree Robotics and EngineAI, race ahead.
"I haven't given much thought to how many robots we will sell annually in 10 years' time, but I think it would be more than cars," XPeng CEO He Xiaopeng told reporters.
XPeng's robots walk and even dance autonomously -- but how well they handle objects, a more complicated feat, has not been widely demonstrated.
Their dexterous fingers and flexible skin are unlikely to replace workers on China's factory floors soon, he said.
The cost of one robot hand, which needs to be replaced regularly for heavy-duty work, could pay a Chinese worker's salary for years.
But with enough data and training, AI humanoid robots could one day perform "almost any human role", from nanny to home chef or gardener, XPeng co-president Brian Gu told AFP.
Text-based AI tools like ChatGPT are trained on huge volumes of words, but physical AI models must also grapple with vision and the spatial relationship between objects.
For now, remotely operating AI robots to teach them how to do something like picking up a cup "is by far the most reliable way to collect data", Yamamoto said.
Just 30 to 50 demonstrations of each task are needed to fine-tune "vision-language-action" AI models, he added.
Enactic has approached several dozen care facilities in Japan to propose that its teleoperated robots take over menial tasks, so qualified care workers have more time to look after elderly residents.
This on-the-job experience will train physical AI models so the robots can act autonomously in future, Yamamoto said.
US-Norwegian startup 1X is taking a similar approach for its humanoid home helper NEO, which it will deliver to American homes from next year.
NEO costs $20,000 to buy, but so far, its performance is shaky, with one video in US media showing the robot struggling to close a dishwasher door, even when teleoperated.
In another embarrassing moment, a Russian humanoid robot, said to be the country's first, staggered then fell flat on its face as it made its debut on stage earlier this week.
There is currently a "big gap" between robots' AI systems and their physical abilities, which lag behind, said Sara Adela Abad Guaman, assistant professor in robotics at University College London.
"Nature has shown us that in order to adapt to the environment, you need to have the right body," Abad told AFP, giving the example of a mountain goat that stumbles on ice.
Nevertheless, big deals are being struck, even as booming investment in artificial intelligence feeds fears of a stock market bubble.
Japan's SoftBank recently called physical AI its "next frontier" as it said it was buying industrial robot maker ABB Robotics for $5.4 billion.
Automation raises questions about the future of human labor, but Abad is not too worried.
At the end of the day, "our sense of touch is incomparable", she said.