The rising mpox outbreaks in Africa that triggered the World Health Organization’s emergency declaration are largely the result of decades of neglect and the global community’s inability to stop sporadic epidemics among a population with little immunity against the smallpox-related disease, leading African scientists said Tuesday.
According to Dr. Dimie Ogoina, who chaired WHO’s mpox emergency committee, negligence has led to a new, more transmissible version of the virus emerging in countries with few resources to stop outbreaks.
Mpox, also known as monkeypox, had been spreading mostly undetected for years in Nigeria and elsewhere before the disease prompted the 2022 outbreak in more than 70 countries, Ogoina said at a virtual news conference.
“What we are witnessing in Africa now is different from the global outbreak in 2022,” he said. Mpox in Africa is now being spread via sexual transmission as well as through close contact among children, pregnant women and other vulnerable groups.
And while most people over 50 were likely vaccinated against smallpox — which may provide some protection against mpox — that is not the case for Africa’s mostly young population, who Ogoina said were mostly susceptible.
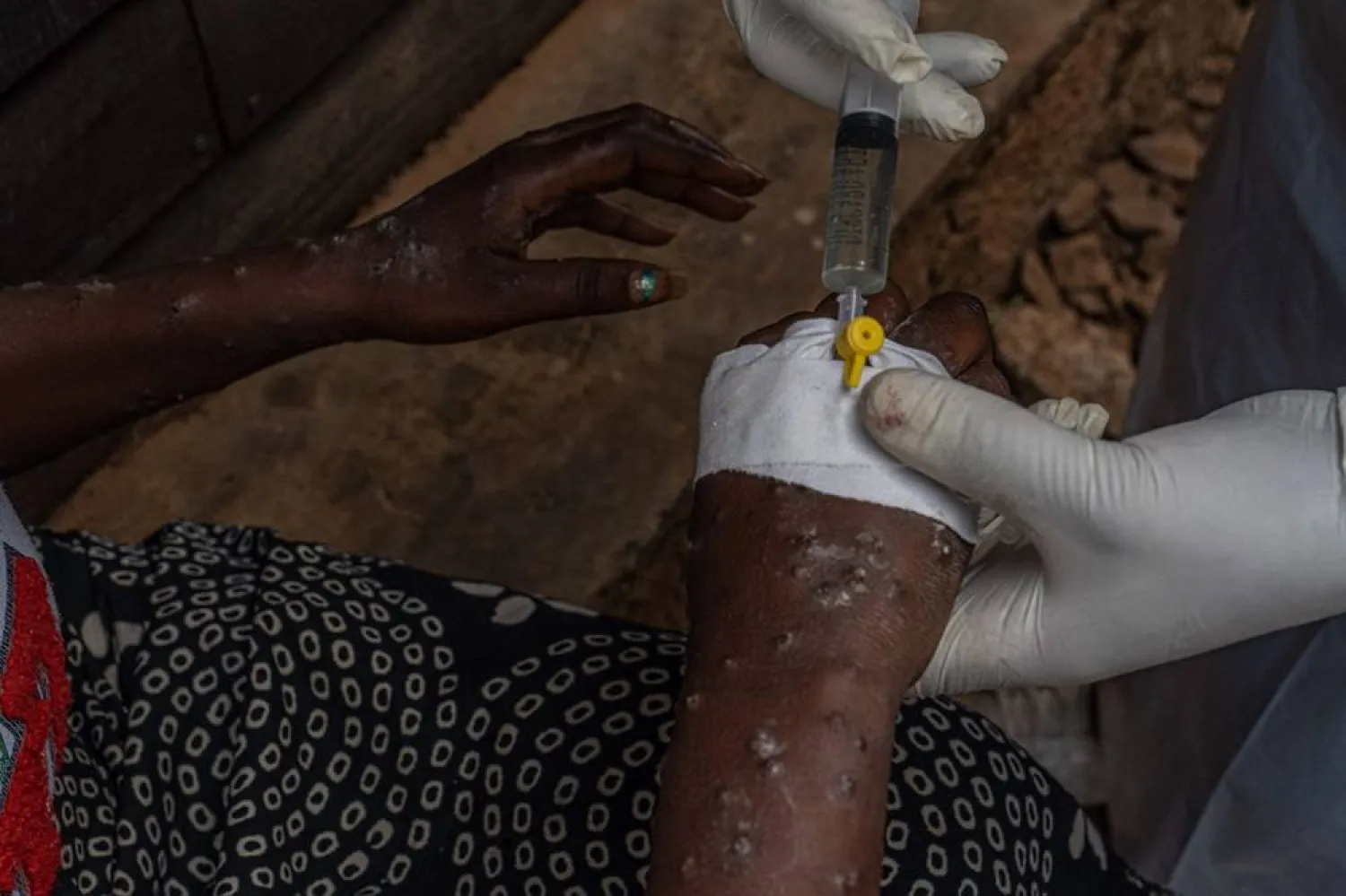
Mpox belongs to the same family of viruses as smallpox but causes milder symptoms like fever and body aches. It mostly spreads through close skin-to-skin contact, including sex. People with more serious cases can develop prominent blisters on the face, hands, chest and genitals.
Earlier this month, WHO declared the surging mpox outbreaks in Congo and 11 other countries in Africa to be a global emergency.
On Tuesday, the Africa Centers for Disease Control and Prevention said there were more than 22,800 mpox cases and 622 deaths on the continent and that infections had jumped 200% in the last week. The majority of cases and deaths are in Congo, where most mpox infections are in children under 15.
Dr. Placide Mbala-Kingebeni, a Congolese scientist who helped identify the newest version of mpox, said diagnostic tests being used in the country did not always pick it up, making it hard to track the variant’s spread.
In May, Mbala-Kingebeni, who heads a lab at Congo’s National Institute for Biomedical Research, published research showing a new form of mpox that may be less deadly but more transmissible. The noted mutations suggested it was “more adapted to human transmission,” he said, but the lack of tests in Congo and elsewhere complicated efforts to monitor outbreaks.
The new variant has been detected in four other African countries as well as Sweden, where health officials said they have identified the first case of a person this month with the more infectious form of mpox. The person had been infected during a stay in Africa.
WHO said that available data to date does not suggest that the new form of mpox is more dangerous but that research is ongoing.
Marion Koopmans, a virologist at Erasmus Medical Centre in the Netherlands who has been studying mpox, said scientists were now seeing some significant impacts of the disease, noting that pregnant women were miscarrying or losing their fetuses and that some babies were being born infected with mpox.
Ogoina, a professor of infectious diseases at Niger Delta University in Nigeria, said that in the absence of vaccines and drugs, African health workers should focus on providing supportive care, like ensuring patients have enough to eat and are given mental health support, given the stigma that often comes with mpox.
“It’s very, very unfortunate that we have had mpox for 54 years and we are only now thinking about therapeutics,” he said.
Mbala-Kingebeni said strategies previously used to stop Ebola outbreaks in Africa might help, given the limited numbers of shots expected. He said authorities have estimated Africa needs about 10 million doses but might only receive about 500,000 — and it’s unclear when they might arrive.
“Finding a case and vaccinating around the case, like we did with Ebola, might help us target the hot spots,” he said.
Koopmans of the Erasmus Medical Centre said that given the urgent need for vaccines in Africa, waiting for more doses to be produced was unrealistic.
“The short term (question) really is about, who has vaccines and where are they to be best used next?" she said.
Spain’s health ministry announced Tuesday that it would dip into its mpox vaccine stockpile to donate 20% of its supply, about 500,000 doses, to African countries battling mpox.
“We consider it senseless to accumulate vaccines where they are not needed,” Spain’s health ministry said in a statement, adding Spain will recommend to the European Commission to propose that all member states also donate 20% of their vaccine stock.
Spain's donation alone is more than what the European Union, vaccine Bavarian Nordic and the US have pledged. Last week, Africa CDC said that the EU and Bavarian Nordic had promised 215,000 mpox vaccines while the US said it had donated 50,000 doses of the same vaccine to Congo. Japan has also donated some doses to Congo.
The Africa CDC said it does not expect any vaccines to land on the continent until next month when political and health leaders meet to discuss how best to pool their limited resources to respond to mpox.